Autonomous circuitry for substrate exploration in freely moving Drosophila larvae
- PMID: 22940472
- PMCID: PMC4082562
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.07.048
Autonomous circuitry for substrate exploration in freely moving Drosophila larvae
Abstract
Background: Many organisms, from bacteria to human hunter-gatherers, use specialized random walk strategies to explore their environment. Such behaviors are an efficient stratagem for sampling the environment and usually consist of an alternation between straight runs and turns that redirect these runs. Drosophila larvae execute an exploratory routine of this kind that consists of sequences of straight crawls, pauses, turns, and redirected crawls. Central pattern generating networks underlying rhythmic movements are distributed along the anteroposterior axis of the nervous system. The way in which the operation of these networks is incorporated into extended behavioral routines such as substrate exploration has not yet been explored. In particular, the part played by the brain in dictating the sequence of movements required is unknown.
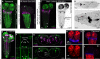
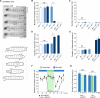
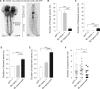
Results: We report the use of a genetic method to block synaptic activity acutely in the brain and subesophageal ganglia (SOG) of larvae during active exploratory behavior. We show that the brain and SOG are not required for the normal performance of an exploratory routine. Alternation between crawls and turns is an intrinsic property of the abdominal and/or thoracic networks. The brain modifies this autonomous routine during goal-directed movements such as those of chemotaxis. Nonetheless, light avoidance behavior can be mediated in the absence of brain activity solely by the sensorimotor system of the abdomen and thorax.
Conclusions: The sequence of movements for substrate exploration is an autonomous capacity of the thoracic and abdominal nervous system. The brain modulates this exploratory routine in response to environmental cues.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
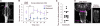

Comment in
-
Behavioral neuroscience: Crawling is a no-brainer for fruit fly larvae.Curr Biol. 2012 Oct 23;22(20):R867-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.08.018. Curr Biol. 2012. PMID: 23098592
References
-
- Berg HC, Brown DA. Chemotaxis in Escherichia coli analysed by three-dimensional tracking. Nature. 1972;239:500–504. - PubMed
-
- McClellan AD, Hagevik A. Descending control of turning locomotor activity in larval lamprey: neurophysiology and computer modeling. J. Neurophysiol. 1997;78:214–228. - PubMed
-
- Humphries NE, Queiroz N, Dyer JRM, Pade NG, Musyl MK, Schaefer KM, Fuller DW, Brunnschweiler JM, Doyle TK, Houghton JDR, et al. Environmental context explains Lévy and Brownian movement patterns of marine predators. Nature. 2010;465:1066–1069. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

