Identification of unknown protein function using metabolite cocktail screening
- PMID: 22940582
- PMCID: PMC3472112
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2012.07.016
Identification of unknown protein function using metabolite cocktail screening
Abstract
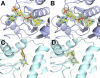
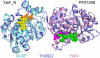
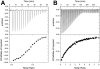
Proteins of unknown function comprise a significant fraction of sequenced genomes. Defining the roles of these proteins is vital to understanding cellular processes. Here, we describe a method to determine a protein function based on the identification of its natural ligand(s) by the crystallographic screening of the binding of a metabolite library, followed by a focused search in the metabolic space. The method was applied to two protein families with unknown function, PF01256 and YjeF_N. The PF01256 proteins, represented by YxkO from Bacillus subtilis and the C-terminal domain of Tm0922 from Thermotoga maritima, were shown to catalyze ADP/ATP-dependent NAD(P)H-hydrate dehydratation, a previously described orphan activity. The YjeF_N proteins, represented by mouse apolipoprotein A-I binding protein and the N-terminal domain of Tm0922, were found to interact with an adenosine diphosphoribose-related substrate and likely serve as ADP-ribosyltransferases. Crystallographic screening of metabolites serves as an efficient tool in functional analyses of uncharacterized proteins.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

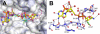


Comment in
-
Fragment and conquer: from structure to complexes to function.Structure. 2012 Oct 10;20(10):1617-9. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2012.09.008. Structure. 2012. PMID: 23063007
References
-
- Acheson SA, Kirkman HN, Wolfenden R. Equilibrium of 5,6-hydration of NADH and mechanism of ATP-dependent dehydration. Biochemistry. 1988;27:7371–7375. - PubMed
-
- Carr R, Jhoti H. Structure-based screening of low-affinity compounds. Drug Discov Today. 2002;7:522–527. - PubMed
-
- Cheng G, Bennett EM, Begley TP, Ealick SE. Crystal structure of 4-amino-5-hydroxymethyl-2-methylpyrimidine phosphate kinase from Salmonella typhimurium at 2.3 A resolution. Structure. 2002;10:225–235. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

