Pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis: two case reports and review of the literature
- PMID: 22941890
- PMCID: PMC9487337
- DOI: 10.1183/09059180.00009411
Pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis: two case reports and review of the literature
Abstract
Pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis is a rare diffuse lung disease characterised by deposition of calcium phosphate within the alveolar airspaces. The disease is usually discovered from birth up to 40 yrs of age and is often diagnosed incidentally during radiography of the chest for other reasons. Many patients are asymptomatic and the majority of patients either have normal or restrictive pulmonary function. The clinical course of the disease varies. While it remains static in some patients, it progresses into pulmonary fibrosis, respiratory failure and cor pulmonale in others. With the exception of lung transplantation, there is no known effective treatment for the disease. Although the aetiology remains unclear, mutations of the solute carrier family 34 (sodium phosphate), member 2 gene (the SLC34A2 gene), which encodes a sodium/phosphate co-transporter, are considered to be the cause of the disease. We present two cases of pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis with different mutations in the SLC34A2 gene that have not been previously described, and a review of the literature.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
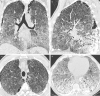
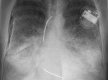

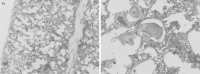
References
-
- Puhr L. Mikrolithiasis alveolaris pulmonum. [Pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis]. Virchows Arch (Pathol Anat) 1933; 290: 156.
-
- Chan ED, Morales DV, Welsh CH, et al. . Calcium deposition with or without bone formation in the lung. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002; 165: 1654–1669. - PubMed
-
- Edelman JD, Bavaria J, Kaiser LR, et al. . Bilateral sequential lung transplantation for pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis. Chest 1997; 112: 1140–1144. - PubMed
-
- Ozcelik U, Gulsun M, Gocmen A, et al. . Treatment and follow-up of pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis with disodium editronate: radiological demonstration. Pediatr Radiol 2002; 32: 380–383. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
