Mycobacterium tuberculosis prokaryotic ubiquitin-like protein-deconjugating enzyme is an unusual aspartate amidase
- PMID: 22942282
- PMCID: PMC3481346
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.384784
Mycobacterium tuberculosis prokaryotic ubiquitin-like protein-deconjugating enzyme is an unusual aspartate amidase
Abstract
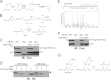
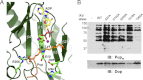
Deamidase of Pup (Dop), the prokaryotic ubiquitin-like protein (Pup)-deconjugating enzyme, is critical for the full virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and is unique to bacteria, providing an ideal target for the development of selective chemotherapies. We used a combination of genetics and chemical biology to characterize the mechanism of depupylation. We identified an aspartate as a potential nucleophile in the active site of Dop, suggesting a novel protease activity to target for inhibitor development.
Figures
References
-
- Striebel F., Imkamp F., Sutter M., Steiner M., Mamedov A., Weber-Ban E. (2009) Bacterial ubiquitin-like modifier Pup is deamidated and conjugated to substrates by distinct but homologous enzymes. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 16, 647–651 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

