Comparative evaluation of local anaesthesia with adrenaline and without adrenaline on blood glucose concentration in patients undergoing tooth extractions
- PMID: 22942593
- PMCID: PMC3238546
- DOI: 10.1007/s12663-011-0239-4
Comparative evaluation of local anaesthesia with adrenaline and without adrenaline on blood glucose concentration in patients undergoing tooth extractions
Abstract
Background: Lignocaine hydrochloride is the most widely used and easily available local anaesthetic agent. Adrenaline is frequently combined with lignocaine to enhance the duration of anaesthesia, decrease toxicity, to achieve vasoconstriction and to provide a bloodless field.
Aim and objective: This study was conducted to do the comparative evaluation of local anaesthesia with adrenaline and without adrenaline on blood glucose concentration in patients under going tooth extraction.
Materials and method: The study was conducted on 120 patients comprising of 60 healthy and 60 diabetic patients. All these patients were in need of multiple extractions. The patients were in the age group of 18-50 years. On their first visit the patients were given plain lignocaine and tooth extraction was carried out. One week later the same patient was given lignocaine with 1:80,000 adrenaline to carry out tooth extraction. Serial blood glucose estimations were done at definite intervals (prior to administration of local anaesthetic, immediately after injecting the LA, 10 and 20 min following the injection of LA) on both the occasions.
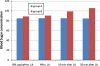
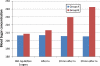
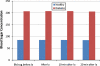
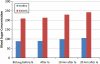
Results: The mean blood glucose concentration increased from the base line level of 84.81 to 85.09 mg/dl in healthy patients and from 206.82 to 207.09 mg/dl in diabetic patients 10 min following the injection of 2% plain lignocaine. This increase in blood glucose concentration following the administration of plain lignocaine was statistically not significant (P > 0.05). There was statistically significant (P < 0.005) increase in the blood glucose concentration from 88.81 to 105.55 mg/dl in healthy, and 208.77 to 242.46 mg/dl in diabetic patients 20 min following the injection of lignocaine with adrenaline.
Interpretation and conclusion: While assessing the generalized effects of local anaesthetic solutions, metabolic as well as haemodynamic responses should be investigated. Adrenaline containing LA should be used with caution in Type 2 diabetics as adrenaline causes suppression of insulin release.
Keywords: Adrenaline; Blood glucose concentration; Diabetic; Lignocaine.
Figures
References
-
- Davenport RE, Porcelli RJ, Lacono JV. Effects of anaesthesia containing epinephrine on catecholamine levels during periodontal surgery. J Periodontol. 1990;61:553–558. - PubMed
-
- Raymond AD, David SG. Effects of diazepam premedication and epinephrine containing local anaesthesia on cardiovascular and plasma catecholamine responses to oral surgery. Anaesth Analg. 1984;63:640–643. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
