Downregulation of VEGF mRNA expression by triamcinolone acetonide acetate-loaded chitosan derivative nanoparticles in human retinal pigment epithelial cells
- PMID: 22942646
- PMCID: PMC3428247
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S29690
Downregulation of VEGF mRNA expression by triamcinolone acetonide acetate-loaded chitosan derivative nanoparticles in human retinal pigment epithelial cells
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this study was to investigate the downregulation of mRNA expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) by triamcinolone acetonide acetate (TAA)-loaded chitosan nanoparticles in human retinal pigment epithelial cells.
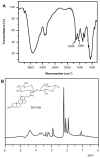
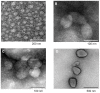
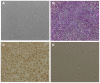
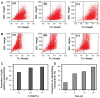
Methods: TAA-loaded deoxycholic acid-modified chitosan (TAA/DA-Chit) nanoparticles were prepared via a self-assembly mechanism, and their morphology and zeta potential were examined by transmission electron microscopy and zeta potential analysis, respectively. DA-Chit and TAA/DA-Chit nanoparticle toxicity was evaluated using a Cell Counting Kit-8 assay. The efficiency of cellular uptake was determined using fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled DA-Chit nanoparticles, in place of TAA/DA-Chit nanoparticles, assessed by both inverted fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry. Downregulation of VEGF mRNA expression by TAA/DA-Chit nanoparticles was further investigated by real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) assay of the treated human retinal pigment epithelial cells.
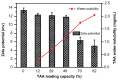
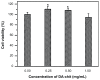
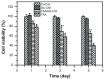
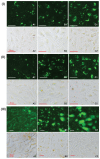
Results: TAA/DA-Chit nanoparticles were prepared with a TAA-loading capacity in the range of 12%-82%, which increased the water solubility of TAA from 0.3 mg/mL to 2.1 mg/mL. These nanoparticles showed oblate shapes 100-550 nm in size in transmission electron microscopic images and had positive zeta potentials. The Cell Counting Kit-8 assay indicated that the DA-Chit and TAA/DA-Chit nanoparticles had no toxicity and low toxicity, respectively, to human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled DA-Chit nanoparticle uptake by human retinal pigment epithelial cells was confirmed by inverted fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry. Real-time RT-PCR assay showed that the VEGF mRNA level decreased after incubation of human retinal pigment epithelial cells with TAA/DA-Chit nanoparticles.
Conclusion: TAA/DA-Chit nanoparticles had a downregulating effect on VEGF mRNA expression in human retinal pigment epithelial cells and low cytotoxicity, which might be beneficial characteristics for the development of future treatment for diabetic retinopathy.
Keywords: chitosan; human retinal pigment epithelial cells; mRNA; nanoparticle; triamcinolone acetonide acetate; vascular endothelial growth factor.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Efficient downregulation of VEGF in retinal pigment epithelial cells by integrin ligand-labeled liposome-mediated siRNA delivery.Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:2613-27. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S39622. Epub 2013 Jul 22. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013. PMID: 23901275 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of curcumin nanoparticles on proliferation and VEGF expression of human retinal pigment epithelial cells.Int J Ophthalmol. 2022 Jun 18;15(6):905-913. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2022.06.07. eCollection 2022. Int J Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35814903 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of scutellarin oral delivery efficacy by vitamin B12-modified amphiphilic chitosan derivatives to treat type II diabetes induced-retinopathy.J Nanobiotechnology. 2017 Mar 1;15(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s12951-017-0251-z. J Nanobiotechnology. 2017. PMID: 28249594 Free PMC article.
-
Triamcinolone acetonide suppresses early proangiogenic response in retinal pigment epithelial cells after photodynamic therapy in vitro.Br J Ophthalmol. 2007 Jan;91(1):100-4. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2006.098004. Epub 2006 Sep 20. Br J Ophthalmol. 2007. PMID: 16987905 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of triamcinolone on the expression of VEGF and PEDF in human retinal pigment epithelial and human umbilical vein endothelial cells.Mol Vis. 2006 Dec 4;12:1490-5. Mol Vis. 2006. PMID: 17167405
Cited by
-
Rapid and Effective Removal of Cu2+ from Aqueous Solution Using Novel Chitosan and Laponite-Based Nanocomposite as Adsorbent.Polymers (Basel). 2016 Dec 27;9(1):5. doi: 10.3390/polym9010005. Polymers (Basel). 2016. PMID: 30970682 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Microglia in Diabetic Retinopathy: Inflammation, Microvasculature Defects and Neurodegeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jan 1;19(1):110. doi: 10.3390/ijms19010110. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29301251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of microglia in diabetic retinopathy.J Ophthalmol. 2014;2014:705783. doi: 10.1155/2014/705783. Epub 2014 Aug 31. J Ophthalmol. 2014. PMID: 25258680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficient delivery of NF-κB siRNA to human retinal pigment epithelial cells with hyperbranched cationic polysaccharide derivative-based nanoparticles.Int J Nanomedicine. 2015 Apr 7;10:2735-49. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S75188. eCollection 2015. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015. PMID: 25897219 Free PMC article.
-
Gene therapy for ocular diseases meditated by ultrasound and microbubbles (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2015 Oct;12(4):4803-14. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.4054. Epub 2015 Jul 7. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 26151686 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Scanlon PH. Diabetic retinopathy. Medicine. 2010;38:656–660.
-
- Fante RJ, Durairaj VD, Oliver SCN. Diabetic retinopathy: An update on treatment. Am J Med. 2010;123:213–216. - PubMed
-
- Kim YH, Chung IY, Choi MY, et al. Triamcinolone suppresses retinal vascular pathology via a potent interruption of proinflammatory signal-regulated activation of VEGF during a relative hypoxia. Neurobiol Dis. 2007;26:569–576. - PubMed
-
- Chung HS, Harris A, Halter PJ, et al. Regional differences in retinal vascular reactivity. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1999;40:2448–2453. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

