The epsin protein family: coordinators of endocytosis and signaling
- PMID: 22942912
- PMCID: PMC3431554
- DOI: 10.1515/bmc-2011-0060
The epsin protein family: coordinators of endocytosis and signaling
Abstract
The epsins are a conserved family of endocytic adaptors essential for cell viability in yeast and for embryo development in higher eukaryotes. Epsins function as adaptors by recognizing ubiquitinated cargo and as endocytic accessory proteins by contributing to endocytic network stability/regulation and membrane bending. Importantly, epsins play a critical role in signaling by contributing to epidermal growth factor receptor downregulation and the activation of notch and RhoGTPase pathways. In this review, we present an overview of the epsins and emphasize their functional importance as coordinators of endocytosis and signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The author stated that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures
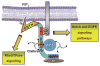

Similar articles
-
Epsin Family of Endocytic Adaptor Proteins as Oncogenic Regulators of Cancer Progression.J Can Res Updates. 2013 Jul 1;2(3):144-150. doi: 10.6000/1929-2279.2013.02.03.2. J Can Res Updates. 2013. PMID: 24501612 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial epsin deficiency decreases tumor growth by enhancing VEGF signaling.J Clin Invest. 2012 Dec;122(12):4424-38. doi: 10.1172/JCI64537. Epub 2012 Nov 26. J Clin Invest. 2012. PMID: 23187125 Free PMC article.
-
The association of epsin with ubiquitinated cargo along the endocytic pathway is negatively regulated by its interaction with clathrin.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Feb 22;102(8):2766-71. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0409719102. Epub 2005 Feb 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15701696 Free PMC article.
-
Epsin: inducing membrane curvature.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007;39(10):1765-70. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2006.12.004. Epub 2007 Jan 17. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17276129 Review.
-
Regulation of membrane protein transport by ubiquitin and ubiquitin-binding proteins.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2003;19:141-72. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.19.110701.154617. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2003. PMID: 14570567 Review.
Cited by
-
EPSIN1 and MTV1 define functionally overlapping but molecularly distinct trans-Golgi network subdomains in Arabidopsis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Oct 13;117(41):25880-25889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2004822117. Epub 2020 Sep 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32989160 Free PMC article.
-
Asian-European differentiation of schizophrenia-associated genes driven by admixture and natural selection.iScience. 2024 Mar 26;27(5):109560. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109560. eCollection 2024 May 17. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38638564 Free PMC article.
-
The Information Content of Glutamine-Rich Sequences Define Protein Functional Characteristics.Proc IEEE Inst Electr Electron Eng. 2017 Feb;105(2):385-393. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2016.2613076. Epub 2016 Dec 1. Proc IEEE Inst Electr Electron Eng. 2017. PMID: 32963411 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin-dependent sorting in endocytosis.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014 Jan 1;6(1):a016808. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a016808. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014. PMID: 24384571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bivalent Motif-Ear Interactions Mediate the Association of the Accessory Protein Tepsin with the AP-4 Adaptor Complex.J Biol Chem. 2015 Dec 25;290(52):30736-49. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.683409. Epub 2015 Nov 5. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26542808 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wendland B. Epsins: adaptors in endocytosis? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3:971–7. - PubMed
-
- Fischer JA, Leavell SK, Li QH. Mutagenesis screens for interacting genes reveal three roles for fat facets during Drosophila eye development. Dev Genet. 1997;21:167–74. - PubMed
-
- Cadavid ALM, Ginzel A, Fischer JA. The function of the Drosophila fat facets deubiquitinating enzyme in limiting photoreceptor cell number is intimately associated with endocytosis. Development. 2000;127:1727–36. - PubMed
-
- Tian X, Hansen D, Schedl T, Skeath JB. Epsin potentiates notch pathway activity in Drosophila and C. elegans Development. 2004;131:5807–15. - PubMed
-
- Chen H, Ko G, Zatti A, Di Giacomo G, Liu L, Raiteri E, Perucco E, Collesi C, Min W, Zeiss C, De Camilli P, Cremona O. Embryonic arrest at midgestation and disruption of notch signaling produced by the absence of both epsin 1 and epsin 2 in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:13838–43. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
