Bacterial brain abscess in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma following radiotherapy: microbiology, clinical features and therapeutic outcomes
- PMID: 22943134
- PMCID: PMC3482557
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-12-204
Bacterial brain abscess in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma following radiotherapy: microbiology, clinical features and therapeutic outcomes
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to analyze the clinical features, causative pathogens, neuro-imaging findings, and therapeutic outcomes of bacterial brain abscess in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) following radiotherapy.
Methods: NPC patients with bacterial brain abscess were evaluated. Their clinical data were collected over a 22-year period. For comparison, the clinical features, causative pathogens, neuro-imaging findings, and therapeutic outcomes between NPC and non-NPC patients were analyzed.
Results: NPC accounted for 5.7% (12/210) of the predisposing factors, with Viridans streptococci and Staphylococcus aureus as the two most common causative pathogens. Significant statistical analysis between the two groups (NPC and non-NPC patients) included chronic otitis media (COM) as the underlying disease, post-radiation necrosis by neuro-imaging, and the temporal lobe as the most common site of brain abscesses. The fatality rate in patients with and without NPC was 16.7% and 20.7%, respectively.
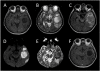
Conclusions: NPC patients with bacterial brain abscess frequently have COM as the underlying disease. Neuro-imaging often reveals both post-radiation necrosis and the temporal lobe as the most common site of brain abscesses, the diagnosis of which is not always a straightforward process. Radiation necrosis can mimic brain abscess on neuro-imaging and pose significant diagnostic challenges. Early diagnosis and treatment is essential for survival.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Management outcome of NPC-related and non-NPC-related brain abscess in Hong Kong.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2012 Jul;114(6):560-3. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2011.11.028. Epub 2011 Dec 16. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2012. PMID: 22178290
-
Bacterial brain abscess formation in post-irradiated patients: What is the possible pathogenesis?Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2015 Sep;136:132-8. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2015.05.025. Epub 2015 Jun 9. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2015. PMID: 26099700
-
Radiation-induced abnormal cortical thickness in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma after radiotherapy.Neuroimage Clin. 2017 Mar 2;14:610-621. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2017.02.025. eCollection 2017. Neuroimage Clin. 2017. PMID: 28348952 Free PMC article.
-
The angiographic and clinical outcomes of intracranial aneurysms following irradiation in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A 13-year experience and literature review.J Neuroradiol. 2018 Jul;45(4):224-229. doi: 10.1016/j.neurad.2018.01.056. Epub 2018 Feb 21. J Neuroradiol. 2018. PMID: 29474882 Review.
-
Treatment of intractable epistaxis in patients with nasopharyngeal cancer.Ann Med. 2023 Dec;55(1):2200257. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2023.2200257. Ann Med. 2023. PMID: 37074291 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Brain Abscess Following Definitive Radiotherapy in Patients With External Auditory Canal Carcinoma: Report of Two Cases.Cureus. 2025 Apr 1;17(4):e81592. doi: 10.7759/cureus.81592. eCollection 2025 Apr. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40322357 Free PMC article.
-
Pediatric Intracranial Abscess From Sinusitis Leading to Status Epilepticus: A Clinical Case Report.Cureus. 2024 Jan 11;16(1):e52116. doi: 10.7759/cureus.52116. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38344593 Free PMC article.
-
A review of the auditory-gut-brain axis.Front Neurosci. 2023 Aug 3;17:1183694. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1183694. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37600010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subdural empyema complicated with intracranial hemorrhage in a postradiotherapy nasopharyngeal carcinoma patient: A case report and review of literature.World J Clin Cases. 2018 Nov 26;6(14):825-829. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i14.825. World J Clin Cases. 2018. PMID: 30510950 Free PMC article.
-
Concurrence of multiple CNS complications in a post-irradiated nasopharyngeal cancer patient.Neurol Sci. 2018 Aug;39(8):1489-1490. doi: 10.1007/s10072-018-3310-9. Epub 2018 Mar 10. Neurol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29525982 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

