Basic fibroblast growth factor protects C17.2 cells from radiation-induced injury through ERK1/2
- PMID: 22943143
- PMCID: PMC6493635
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2012.00365.x
Basic fibroblast growth factor protects C17.2 cells from radiation-induced injury through ERK1/2
Abstract
Aims: To establish a radiation-induced neural injury model using C17.2 neural stem cells (NSCs) and to investigate whether basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) can protect the radiation-induced injury of C17.2 NSCs. Furthermore, we aim to identify the possible mechanisms involved in this model.
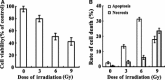
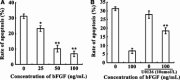
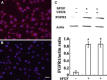
Methods: C17.2 NSCs received a single exposure (3, 6, and 9 Gy, respectively) at a dose rate of 300 cGy/min with a control group receiving 0 Gy. Different concentrations of bFGF were added for 24 h, 5 min postirradiation. The MTS assay and flow cytometry were used to detect cytotoxicity and apoptosis. Expression of FGFR1, ERK1/2, and p-ERK1/2 proteins was detected with or without U0126 was pretreated prior to C17.2 NSCs receiving irradiation.
Results: C17.2 NSCs showed a dose-dependent cell death as the dose of radiation was increased. Additionally, the rate of apoptosis in the C17.2 NSCs reached 31.2 ± 1.23% in the 6 Gy irradiation group, which was the most significant when compared to the other irradiation treated groups. bFGF showed protective effect on cell apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner. The mean percentage of apoptotic cells decreased to 7.83 ± 1.75% when 100 ng/mL bFGF was given. Furthermore, U0126 could block the protective effect of bFGF by inhibiting the phosphorylation of ERK1/2.
Conclusions: An in vitro cellular model of radiation-induced apoptosis of NSCs, in C17.2 NSCs, was developed successfully. Additionally, bFGF can protect neurons from radiation injury in vitro via the ERK1/2 signal transduction pathway.
© 2012 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
PDGF-BB and bFGF ameliorate radiation-induced intestinal progenitor/stem cell apoptosis via Akt/p53 signaling in mice.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014 Dec 1;307(11):G1033-43. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00151.2014. Epub 2014 Oct 9. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25301184
-
Basic fibroblast growth factor inhibits radiation-induced apoptosis of HUVECs. II. The RAS/MAPK pathway and phosphorylation of BAD at serine 112.Radiat Res. 2004 Jun;161(6):703-11. doi: 10.1667/rr3159. Radiat Res. 2004. PMID: 15161349
-
Dose-dependent short- and long-term effects of ionizing irradiation on neural stem cells in murine hippocampal tissue cultures: neuroprotective potential of resveratrol.Brain Behav. 2016 Aug 12;6(10):e00548. doi: 10.1002/brb3.548. eCollection 2016 Oct. Brain Behav. 2016. PMID: 27781151 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous basic fibroblast growth factor protects the lung but not mediastinal organs against radiation-induced apoptosis in vivo.Cancer J Sci Am. 1995 May-Jun;1(1):62-72. Cancer J Sci Am. 1995. PMID: 9166456
-
Upregulation of Flk-1 by bFGF via the ERK pathway is essential for VEGF-mediated promotion of neural stem cell proliferation.Cell Res. 2007 Jan;17(1):73-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.cr.7310126. Epub 2007 Jan 9. Cell Res. 2007. PMID: 17211450
Cited by
-
Curcumin inhibits oxidative stress and autophagy in C17.2 neural stem cell through ERK1/2 signaling pathways.Aging Med (Milton). 2024 Oct 13;7(5):559-570. doi: 10.1002/agm2.12361. eCollection 2024 Oct. Aging Med (Milton). 2024. PMID: 39507234 Free PMC article.
-
Once the Light Touch to the Brain: Cytotoxic Effects of Low-Dose Gamma-Ray, Laser Light, and Visible Light on Rat Neuronal Cell Culture.Eurasian J Med. 2016 Jun;48(2):76-83. doi: 10.5152/eurasianjmed.2015.0304. Eurasian J Med. 2016. PMID: 27551168 Free PMC article.
-
Edaravone protects HT22 neurons from H2O2-induced apoptosis by inhibiting the MAPK signaling pathway.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2013 Mar;19(3):163-9. doi: 10.1111/cns.12044. Epub 2012 Dec 18. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2013. PMID: 23253171 Free PMC article.
-
The antiaging activity and cerebral protection of rapamycin at micro-doses.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2014 Nov;20(11):991-8. doi: 10.1111/cns.12338. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2014. PMID: 25327787 Free PMC article.
-
PI3K/Akt/FoxO3a signaling mediates cardioprotection of FGF-2 against hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis in H9c2 cells.Mol Cell Biochem. 2016 Mar;414(1-2):57-66. doi: 10.1007/s11010-016-2658-5. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Mol Cell Biochem. 2016. PMID: 26899709
References
-
- Tsao MN, Lloyd NS, Wong RK, Rakovitch E, Chow E, Laperriere N. Radiotherapeutic management of brain metastases: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Cancer Treat Rev 2005;31: 256–273. - PubMed
-
- Kantor G, Laprie A, Huchet A, Loiseau H, Dejean C, Mazeron JJ. Radiation therapy for glial tumors: technical aspects and clinical indications. Cancer Radiother 2008;12: 687–694. - PubMed
-
- Crossen JR, Garwood D, Glatstein E, Neuwelt EA. Neurobehavioral sequelae of cranial irradiation in adults: a review of radiation‐induced encephalopathy. J Clin Oncol 1994;12: 627–642. - PubMed
-
- Schultheiss TE, Kun LE, Ang KK, Stephens LC. Radiation response of the central nervous system. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1995;31: 1093–1112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

