Inhibition of DNA methyltransferase activity and expression by treatment with the pan-deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines
- PMID: 22943463
- PMCID: PMC3487800
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-12-386
Inhibition of DNA methyltransferase activity and expression by treatment with the pan-deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) still represents an unmet medical need. Epigenetic inactivation of tumor suppressor genes like RASSF1A or APC by overexpression of DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) has been shown to be common in HCC and to be linked to the overall prognosis of patients. Inhibitors of protein and histone deacetylases (DACi) have been demonstrated to possess strong anti-tumor effects in HCC models.
Methods: We therefore investigated whether DACi also has any influence on the expression and activity of DNMTs and methylated target genes in HepG2 and Hep3B cell culture systems and in a xenograft model by immunohistochemistry, westernblotting, RT-qPCR and methylation-specific PCR.
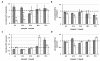
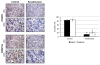
Results: Our findings demonstrate a rapid inhibition of DNMT activity 6 h after treatment with 0.1 μM of the pan-DACi panobinostat. A downregulation of DNMT mRNAs and protein were also observed at later points in time. This loss of DNMT activity and expression was paralleled by a diminished methylation of the target genes RASSF1A and APC and a concomitant re-expression of APC mRNA and protein. Analysis of HepG2 xenograft specimens confirmed these results in vivo.
Conclusion: We suggest a dual mode of action of DACi on DNA methylation status: a rapid inhibition of enzyme activity due to interference with posttranslational acetylation and a delayed effect on transcriptional control of DNMT genes by HDAC or miRNA mechanisms.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The pan-deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat suppresses the expression of oncogenic miRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines.Mol Carcinog. 2015 Aug;54(8):585-97. doi: 10.1002/mc.22122. Epub 2013 Dec 23. Mol Carcinog. 2015. PMID: 24375802
-
The pan-deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat affects angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma models via modulation of CTGF expression.Int J Oncol. 2015 Sep;47(3):963-70. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2015.3087. Epub 2015 Jul 16. Int J Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26202945
-
Downregulation of HMGA2 by the pan-deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat is dependent on hsa-let-7b expression in liver cancer cell lines.Exp Cell Res. 2012 Sep 10;318(15):1832-43. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2012.04.018. Epub 2012 Jun 8. Exp Cell Res. 2012. PMID: 22683924
-
Deacetylase inhibitors: an advance in myeloma therapy?Expert Rev Hematol. 2017 Mar;10(3):229-237. doi: 10.1080/17474086.2017.1280388. Epub 2017 Feb 1. Expert Rev Hematol. 2017. PMID: 28076695 Review.
-
Epigenetic therapy in cancer: molecular background and clinical development of histone deacetylase and DNA methyltransferase inhibitors.IDrugs. 2007 Aug;10(8):557-61. IDrugs. 2007. PMID: 17665331 Review.
Cited by
-
Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors in the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Current Evidence and Future Opportunities.J Pers Med. 2021 Mar 22;11(3):223. doi: 10.3390/jpm11030223. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 33809844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Modifications in Thyroid Cancer Cells Restore NIS and Radio-Iodine Uptake and Promote Cell Death.J Clin Med. 2018 Mar 21;7(4):61. doi: 10.3390/jcm7040061. J Clin Med. 2018. PMID: 29561759 Free PMC article.
-
Modification of Epigenetic Histone Acetylation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2018 Jan 3;10(1):8. doi: 10.3390/cancers10010008. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29301348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Changes Affecting the Development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Aug 23;13(16):4237. doi: 10.3390/cancers13164237. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34439391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis B virus infection in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues upregulates expression of DNA methyltransferases.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Mar 15;8(3):4175-85. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26064328 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

