Polymeric micelles and alternative nanonized delivery vehicles for poorly soluble drugs
- PMID: 22944304
- PMCID: PMC3760723
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2012.08.042
Polymeric micelles and alternative nanonized delivery vehicles for poorly soluble drugs
Abstract
Poorly soluble drugs often encounter low bioavailability and erratic absorption patterns in the clinical setting. Due to the rising number of compounds having solubility issues, finding ways to enhance the solubility of drugs is one of the major challenges in the pharmaceutical industry today. Polymeric micelles, which form upon self-assembly of amphiphilic macromolecules, can act as solubilizing agents for delivery of poorly soluble drugs. This manuscript examines the fundamentals of polymeric micelles through reviews of representative literature and demonstrates possible applications through recent examples of clinical trial developments. In particular, the potential of polymeric micelles for delivery of poorly water-soluble drugs, especially in the areas of oral delivery and in cancer therapy, is discussed. Key considerations in utilizing polymeric micelles' advantages and overcoming potential disadvantages have been highlighted. Lastly, other possible strategies related to particle size reduction for enhancing solubilization of poorly water-soluble drugs are introduced.
Keywords: Anticancer; Clinical trial; Drug solubilization; Micelle stability; Nanocrystal; Nanoemulsion; Oral delivery; Polymeric micelle.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

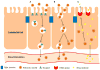
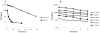
Similar articles
-
Recent Advances in Drug Delivery of Polymeric Nano-Micelles.Curr Drug Metab. 2017;18(1):16-29. doi: 10.2174/1389200217666160921143616. Curr Drug Metab. 2017. PMID: 27654898
-
Hydrotropic polymer micelles as versatile vehicles for delivery of poorly water-soluble drugs.J Control Release. 2011 May 30;152(1):13-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2011.02.014. Epub 2011 Feb 23. J Control Release. 2011. PMID: 21352878
-
Assessing the pharmacokinetics and toxicology of polymeric micelle conjugated therapeutics.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2021 Mar;17(3):323-332. doi: 10.1080/17425255.2021.1862085. Epub 2020 Dec 21. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33292023 Review.
-
Polymeric micelles: nanocarriers for cancer-targeted drug delivery.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2014 Aug;15(4):862-71. doi: 10.1208/s12249-014-0113-z. Epub 2014 Apr 4. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2014. PMID: 24700296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymeric micelles for the delivery of poorly soluble drugs: From nanoformulation to clinical approval.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020;156:80-118. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2020.09.009. Epub 2020 Sep 24. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020. PMID: 32980449 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nanoparticles Targeting STATs in Cancer Therapy.Cells. 2019 Sep 27;8(10):1158. doi: 10.3390/cells8101158. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31569687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional nano-systems for transdermal drug delivery and skin therapy.Nanoscale Adv. 2023 Feb 24;5(6):1527-1558. doi: 10.1039/d2na00530a. eCollection 2023 Mar 14. Nanoscale Adv. 2023. PMID: 36926556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biochemistry of Antioxidants: Mechanisms and Pharmaceutical Applications.Biomedicines. 2022 Nov 25;10(12):3051. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10123051. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36551806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymeric micelles, a promising drug delivery system to enhance bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs.J Drug Deliv. 2013;2013:340315. doi: 10.1155/2013/340315. Epub 2013 Jun 27. J Drug Deliv. 2013. PMID: 23936656 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of the role of nanotechnological innovations in the detection and treatment of solid tumors.Int J Nanomedicine. 2014 Jan 22;9:589-613. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S50941. eCollection 2014. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014. PMID: 24489467 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lipinski C. Drug-like properties and the causes of poor solubility and poor permeability. Journal of Pharmacological and Toxicological Methods. 2000;44(1):235–249. - PubMed
-
- Merisko-Liversidge EM, Liversidge GG. Drug Nanoparticles: Formulating Poorly Water-Soluble Compounds. Toxicologic Pathology. 2008;36(1):43–48. - PubMed
-
- Horter D, Dressman JB. Influence of physicochemical properties on dissolution of drugs in the gastrointestinal tract. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. 2001;46(1-3):75–87. - PubMed
-
- Kawabata Y, Wada K, Nakatani M, Yamada S, Onoue S. Formulation design for poorly water-soluble drugs based on biopharmaceutics classification system: Basic approaches and practical applications. International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 2011;420(1):1–10. - PubMed
-
- Kawakami K, Yoshikawa T, Moroto Y, Kanaoka E, Takahashi K, Nishihara Y, Masuda K. Microemulsion formulation for enhanced absorption of poorly soluble drugs: I. Prescription design. Journal of Controlled Release. 2002;81(1-2):65–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

