Pseudomonas aeruginosa serology and risk for re-isolation in the EPIC trial
- PMID: 22944725
- PMCID: PMC3696392
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcf.2012.08.001
Pseudomonas aeruginosa serology and risk for re-isolation in the EPIC trial
Abstract
Background: The prognostic value of Pseudomonas aeruginosa serology for antibiotic therapy in cystic fibrosis patients is not well understood.
Methods: Using five antigens from two ELISAs, we assessed whether positive serology in CF patients participating in the multi-center Early Pseudomonas Infection in Children (EPIC) trial would predict treatment failure, time to pulmonary exacerbation and risk for recurrent P. aeruginosa isolation post eradication.
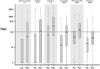
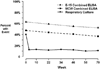
Results: Baseline positive P. aeruginosa serology was not significantly associated with failure of initial P. aeruginosa eradication measured at week 10 (adjusted for baseline culture) but seropositivity to the antigens alkaline protease and exotoxin A was significantly associated with increased risk for recurrent P. aeruginosa isolation during the 60 week post eradication follow-up period (p=0.003 and p=0.001 respectively). There was no association between baseline seropositivity and time to pulmonary exacerbation.
Conclusion: P. aeruginosa serology may complement culture results in clinicians' efforts to successfully monitor recurrence of early P. aeruginosa in CF patients.
Copyright © 2012 European Cystic Fibrosis Society. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Frederiksen B, Koch C, Hoiby N. Antibiotic treatment of initial colonization with Pseudomonas aeruginosa postpones chronic infection and prevents deterioration of pulmonary function in cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1997;23:330–335. - PubMed
-
- Taccetti G, Campana S, Festini F, Mascherini M, Doring G. Early eradication therapy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis patients. Eur Respir J. 2005;26:458–461. - PubMed
-
- Doring G, Hoiby N. Early intervention and prevention of lung disease in cystic fibrosis: a European consensus. J Cyst Fibros. 2004;3:67–91. - PubMed
-
- Rosenfeld M, Gibson RL, McNamara S, Emerson J, Burns JL, Castile R, et al. Early pulmonary infection, inflammation, and clinical outcomes in infants with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2001;32:356–366. - PubMed
-
- Burns JL, Gibson RL, McNamara S, Yim D, Emerson J, Rosenfeld M, et al. Longitudinal assessment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in young childrenwith cystic fibrosis. J Infect Dis. 2001;183:444–452. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

