Modeling of long-term fatigue damage of soft tissue with stress softening and permanent set effects
- PMID: 22945802
- PMCID: PMC3546129
- DOI: 10.1007/s10237-012-0431-6
Modeling of long-term fatigue damage of soft tissue with stress softening and permanent set effects
Abstract
One of the major failure modes of bioprosthetic heart valves is non-calcific structural deterioration due to fatigue of the tissue leaflets. Experimental methods to characterize tissue fatigue properties are complex and time-consuming. A constitutive fatigue model that could be calibrated by isolated material tests would be ideal for investigating the effects of more complex loading conditions. However, there is a lack of tissue fatigue damage models in the literature. To address these limitations, in this study, a phenomenological constitutive model was developed to describe the stress softening and permanent set effects of tissue subjected to long-term cyclic loading. The model was used to capture characteristic uniaxial fatigue data for glutaraldehyde-treated bovine pericardium and was then implemented into finite element software. The simulated fatigue response agreed well with the experimental data and thus demonstrates feasibility of this approach.
Figures


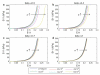

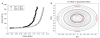



References
-
- Alastrué V, Rodríguez JF, et al. Structural damage models for fibrous biological soft tissues. Int J Solids Struct. 2007;44(18–19):5894–5911.
-
- Broom ND. Fatigue-induced damage in gluteraldehyde-preserved heart valve tissue. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1978;76(2):202–211. - PubMed
-
- Calvo B, Pena E, et al. An uncoupled directional damage model for fibred biological soft tissues. Formulation and computational aspects. Int J Numer Methods Eng. 2007;69(10):2036–2057.
-
- Dorfmann A, Ogden RW. A constitutive model for the Mullins effect with permanent set in particle-reinforced rubber. Int J Solids Struct. 2004;41(7):1855–1878.
-
- Fung YC. Biomechanics: mechanical properties of living tissues. Springer; New York: 1993.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

