The use of group sequential designs with common competing risks tests
- PMID: 22945865
- PMCID: PMC3574186
- DOI: 10.1002/sim.5597
The use of group sequential designs with common competing risks tests
Abstract
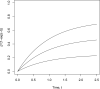
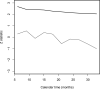
Clinical trials are often performed using a group sequential design in order to allow investigators to review the accumulating data sequentially and possibly terminate the trial early for efficacy or futility. Standard methods for comparing survival distributions have been shown under varying levels of generality to follow an independent increments structure. In the presence of competing risks, where the occurrence of one type of event precludes the occurrence of another type of event, researchers may be interested in inference on the cumulative incidence function, which describes the probability of experiencing a particular event by a given time. This manuscript shows that two commonly used tests for comparing cumulative incidence functions, a pointwise comparison at a single point, and Gray's test, also follow the independent increments structure when used in a group sequential setting. A simulation study confirms the theoretical derivations even for modest trial sample sizes. We used two examples of clinical trials in hematopoietic cell transplantation to illustrate the techniques.
Copyright © 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Jennison C, Turnbull BW. Group sequential Methods with application to clinical trials. Chapman and Hall/CRC; Boca Raton: 2000.
-
- Tsiatis AA. The asymptotic joint distribution of the efficient scores test for the proportional hazards model calculated over time. Biometrika. 1981;68:311–315.
-
- Tsiatis AA, Rosner GL, Tritchler DL. Group sequential tests with censored survival data adjusting for covariates. Biometrika. 1985;72:365–373.
-
- Bilias Y, Gu M, Ying Z. Towards a general asymptotic theory for Cox model with staggered entry. Annals of Statistics. 1996;25:662–682.
-
- Slud EV. Sequential linear rank tests for two-sample censored survival data. Annals of Statistics. 1984;12:551–571.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
