A clinic-based interdisciplinary intervention for mothers of children newly diagnosed with cancer: a pilot study
- PMID: 22946083
- PMCID: PMC3481781
- DOI: 10.1093/jpepsy/jss093
A clinic-based interdisciplinary intervention for mothers of children newly diagnosed with cancer: a pilot study
Abstract
Objective: To determine the feasibility and acceptability of an interdisciplinary intervention for mothers of children newly diagnosed with cancer and to estimate effect sizes for the intervention in reducing distress. Management of illness uncertainty was a key framework for the intervention.
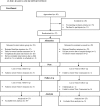
Methods: Mothers (N = 52) were randomly assigned to the intervention or a treatment as usual group, completing measures at baseline and follow-up time points.
Results: Mothers' satisfaction ratings were consistently high, and intervention implementation appeared feasible. Significant mean effects or trends in favor of the intervention group were found for pre-to-post change on measures of distress. Evidence of a preventative effect was also observed; mothers in the intervention group tended to improve or remain stable in their adjustment, whereas many parents in the treatment as usual group showed worsening outcomes.
Conclusions: An interdisciplinary intervention targeting maternal illness uncertainty has clinical value within this sample.
Figures



References
-
- American Cancer Society. Cancer facts & figures 2010. 2010. Retrieved from http://www.cancer.org/downloads/STT/2008CAFFfinalsecured.pdf.
-
- Derogatis LR. Symptom checklist-90-revised: Administration, scoring, and procedures manual. Minneapolis, MN: National Computer Systems, Inc; 1994.
-
- Dwyer K. Beyond cancer: Fostering transitions post-treatment. Bethesda, MD: National Institutes of Health; 2006. Grant #3R21CA100120-02S1.
-
- Fuemmeler B F, Mullins L L, Marx B P. Posttraumatic stress and general distress among parents of children surviving a brain tumor. Children’s Health Care. 2001;30:169–182. doi:10.1207/S15326888CHC3003_1.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

