Age-related influence of vision and proprioception on Ia presynaptic inhibition in soleus muscle during upright stance
- PMID: 22946095
- PMCID: PMC3515837
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.228932
Age-related influence of vision and proprioception on Ia presynaptic inhibition in soleus muscle during upright stance
Abstract
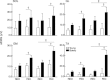
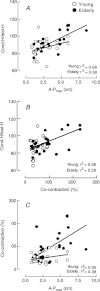
This study investigated the modulation of Ia afferent input in young and elderly adults during quiet upright stance in normal and modified visual and proprioceptive conditions. The surface EMG of leg muscles, recruitment curve of the soleus (SOL) Hoffmann (H) reflex and presynaptic inhibition of Ia afferents from SOL, assessed with the D1 inhibition and single motor unit methods, were recorded when young and elderly adults stood with eyes open or closed on two surfaces (rigid vs. foam) placed over a force platform. The results showed that elderly adults had a longer path length for the centre of pressure and larger antero-posterior body sway across balance conditions (P < 0.05). Muscle EMG activities were greater in elderly compared with young adults (P < 0.05), whereas the H(max) expressed as a percentage of the H(max) was lower (P = 0.048) in elderly (38 ± 16%) than young adults (58 ± 16%). The conditioned H reflex/test H reflex ratio (D1 inhibition method) increased with eye closure and when standing on foam (P < 0.05), with greater increases for elderly adults (P = 0.019). These changes were accompanied by a reduced peak motor unit discharge probability when standing on rigid and foam surfaces (P 0.001), with a greater effect for elderly adults (P = 0.026). Based on these latter results, the increased conditioned H reflex/test H reflex ratio in similar sensory conditions is likely to reflect occlusion at the level of presynaptic inhibitory interneurones. Together, these findings indicate that elderly adults exhibit greater modulation of Ia presynaptic inhibition than young adults with variation in the sensory conditions during upright standing.
Figures




References
-
- Baudry S, Lecoeuvre G, Duchateau J. Age-related changes in the behavior of the muscle-tendon unit of the gastrocnemius medialis during upright stance. J Appl Physiol. 2012;112:296–304. - PubMed
-
- Benjuya N, Melzer I, Kaplanski J. Aging-induced shifts from a reliance on sensory input to muscle cocontraction during balanced standing. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2004;59:166–171. - PubMed
-
- Billot M, Simoneau EM, Van Hoecke J, Martin A. Age-related relative increases in electromyography activity and torque according to the maximal capacity during upright standing. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2010;109:669–680. - PubMed
-
- Burke D, Adams RW, Skuse NF. The effects of voluntary contraction on the H reflex of human limb muscles. Brain. 1989;112:417–433. - PubMed
-
- Capaday C, Lavoie BA, Comeau F. Differential effects of a flexor nerve input on the human soleus H-reflex during standing versus walking. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1995;73:436–449. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

