The natural history of cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 22946521
- PMCID: PMC3534850
- DOI: 10.1037/a0029857
The natural history of cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
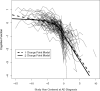
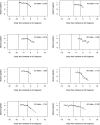
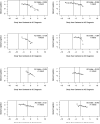
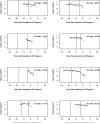
The study aim was to describe the temporal course of cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease (AD). We selected 226 persons from 2 longitudinal clinical-pathological studies who were cognitively healthy at baseline, followed at least 4 years (M = 10.2, SD = 3.5), and clinically diagnosed with AD at some point during follow-up. Each evaluation included a battery of 17 cognitive tests from which a previously established composite measure of global cognition was derived. In those who died, a uniform neuropathologic examination established the pathological diagnoses of Alzheimer's disease and other common conditions that impair cognition. Mixed-effects models with 2 change points were used to assess trajectories of cognitive decline. In the main analysis, there was no change in cognitive function until a mean of 7.5 years before dementia was diagnosed (95% confidence interval [CI]: -8.3, -6.7). The global cognitive measure declined a mean of 0.087-unit per year (95% CI: -0.099, -0.073) until a mean of 2.0 years before the diagnosis (95% CI: -2.2, -1.7) when it increased more than 4-fold to a mean loss of 0.370-unit per year (95% CI: -0.417, -0.334). Of 126 individuals who died and underwent autopsy, 101 (80%) met pathologic criteria for AD, of whom 67 had at least one other pathologic condition. Pathologic measures of AD and cerebral infarction were not strongly related to cognitive trajectories. The results indicate that cognitive decline in AD begins many years before dementia is diagnosed and accelerates during the course of the disease.
2013 APA, all rights reserved
Figures
References
-
- Amieva H, LeGoff M, Millet X, Orgogozo JM, Pérés K, Barberger-Gateau P, Jacqmin-Gadda H, Dartigues JF. Prodromal Alzheimer's disease: Successive emergence of clinical symptoms. Annals of Neurology. 2008;64:492–498. - PubMed
-
- Bäckman L, Small BJ, Fratiglioni L. Stability of the preclinical episodic memory deficit in Alzheimer's disease. Brain. 2001;124:96–102. - PubMed
-
- Bennett DA, Schneider JA, Aggarwal NT, Arvanitakis Z, Shah RC, Kelly JF, Fox JH, Cochran EJ, Arends D, Treinkman AD, Wilson RS. Decision rules guiding the clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease in two community-based cohort studies compared to standard practice in a clinic-based cohort study. Neuroepidemiology. 2006;27:169–176. - PubMed
-
- Bennett DA, Schneider JA, Bienias JL, Evans DA, Wilson RS. Mild cognitive impairment is related to Alzheimer disease pathology and cerebral infarctions. Neurology. 2005;64:834–841. - PubMed
-
- Bennett DA, Schneider JA, Buchman AS, Mendes de Leon C, Bienias JL, Wilson RS. The Rush Memory and Aging Project: Study design and baseline characteristics of the study cohort. Neuroepidemiology. 2005;25:163–175. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

