Calmodulin binds a highly extended HIV-1 MA protein that refolds upon its release
- PMID: 22947870
- PMCID: PMC3414894
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2012.06.042
Calmodulin binds a highly extended HIV-1 MA protein that refolds upon its release
Erratum in
-
Calmodulin Binds a Highly Extended HIV-1 MA Protein That Refolds Upon Its Release.Biophys J. 2023 May 2;122(9):1734. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2023.04.004. Epub 2023 Apr 8. Biophys J. 2023. PMID: 37031681 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
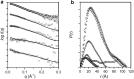
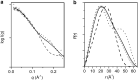
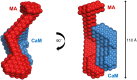
Calmodulin (CaM) expression is upregulated upon HIV-1 infection and interacts with proteins involved in viral processing, including the multifunctional HIV-1 MA protein. We present here the results of studies utilizing small-angle neutron scattering with contrast variation that, when considered in the light of earlier fluorescence and NMR data, show CaM binds MA in an extended open-clamp conformation via interactions with two tryptophans that are widely spaced in sequence and space. The interaction requires a disruption of the MA tertiary fold such that MA becomes highly extended in a long snakelike conformation. The CaM-MA interface is extensive, covering ~70% of the length of the MA such that regions known to be important in MA interactions with critical binding partners would be impacted. The CaM conformation is semiextended and as such is distinct from the classical CaM-collapse about short α-helical targets. NMR data show that upon dissociation of the CaM-MA complex, either by the removal of Ca2+ or increasing ionic strength, MA reforms its native tertiary contacts. Thus, we observe a high level of structural plasticity in MA that may facilitate regulation of its activities via intracellular Ca2+-signaling during viral processing.
Copyright © 2012 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Chin D., Means A.R. Calmodulin: a prototypical calcium sensor. Trends Cell Biol. 2000;10:322–328. - PubMed
-
- Yamniuk A.P., Vogel H.J. Calmodulin's flexibility allows for promiscuity in its interactions with target proteins and peptides. Mol. Biotechnol. 2004;27:33–57. - PubMed
-
- Miller M.A., Mietzner T.A., et al. Montelaro R.C. Identification of a calmodulin-binding and inhibitory peptide domain in the HIV-1 transmembrane glycoprotein. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses. 1993;9:1057–1066. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

