Neuropilins are multifunctional coreceptors involved in tumor initiation, growth, metastasis and immunity
- PMID: 22948112
- PMCID: PMC3660061
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.626
Neuropilins are multifunctional coreceptors involved in tumor initiation, growth, metastasis and immunity
Abstract
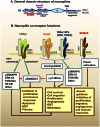
The neuropilins (Nrps) are multifunctional proteins involved in development, immunity and cancer. Neuropilin-1 (Nrp1), or its homologue neuropilin-2 (Nrp2), are coreceptors that enhance responses to several growth factors (GFs) and other mediators. Nrps are coreceptors for the class 3 semaphorins (SEMA3), involved in axonal guidance, and several members of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family. However, recent findings reveal they have a much broader spectrum of activity. They bind transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1) and its receptors, hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and its receptor (cMet), platelet derived growth factor (PDGF) and its receptors, fibroblast growth factors (FGFs), and integrins. Nrps also promote Hedgehog signaling. These ligands and pathways are all relevant to angiogenesis and wound healing. In the immune system, the Nrps are expressed primarily by dendritic cells (DCs) and regulatory T cells (Tregs), and exert mainly inhibitory effects. In cancer, Nrps have been linked to a poor prognosis, which is consistent with their numerous interactions with ligands and receptors that promote tumor progression. We hypothesize that Nrps boost responses by capturing ligands, regulating GF receptor expression, endocytosis and recycling, and possibly also by signaling independently. Importantly, they promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and the survival of cancer stem cells. The recent finding that Nrps bind and internalize cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) with arginine/lysine-rich C-terminal motifs (C-end rule; e.g., RXXR) is of interest. These CPPs can be coupled to large drugs for cancer therapy. Almost all studies have been preclinical, but findings suggest Nrps are excellent targets for anti-cancer drug development.
Figures
Comment in
-
Neurophilin-1 in tumor growth.Oncotarget. 2012 Nov;3(11):1259. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.734. Oncotarget. 2012. PMID: 23175449 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Pellet-Many C, Frankel P, Jia H, Zachary I. Neuropilins: structure, function and role in disease. Biochem J. 2008;411:211–226. - PubMed
-
- Uniewicz KA, Fernig DG. Neuropilins: a versatile partner of extracellular molecules that regulate development and disease. Front Biosci. 2008;13:4339–4360. - PubMed
-
- Romeo PH, Lemarchandel V, Tordjman R. Neuropilin-1 in the immune system. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002;515:49–54. - PubMed
-
- Bruder D, Probst-Kepper M, Westendorf AM, Geffers R, Beissert S, Loser K, von Boehmer H, Buer J, Hansen W. Neuropilin-1: a surface marker of regulatory T cells. Eur J Immunol. 2004;34:623–630. - PubMed
-
- Bielenberg DR, Pettaway CA, Takashima S, Klagsbrun M. Neuropilins in neoplasms: expression, regulation, and function. Exp Cell Res. 2006;312:584–593. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

