HCN1 and HCN2 proteins are expressed in cochlear hair cells: HCN1 can form a ternary complex with protocadherin 15 CD3 and F-actin-binding filamin A or can interact with HCN2
- PMID: 22948144
- PMCID: PMC3488041
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.375832
HCN1 and HCN2 proteins are expressed in cochlear hair cells: HCN1 can form a ternary complex with protocadherin 15 CD3 and F-actin-binding filamin A or can interact with HCN2
Abstract
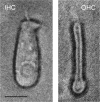
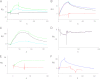
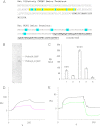
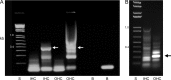
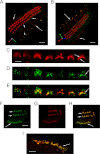
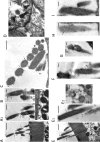
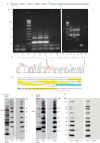
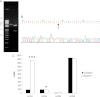
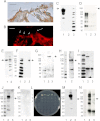
A unique coupling between HCN1 and stereociliary tip-link protein protocadherin 15 has been described for a teleost vestibular hair-cell model and mammalian organ of Corti (OC) (Ramakrishnan, N. A., Drescher, M. J., Barretto, R. L., Beisel, K. W., Hatfield, J. S., and Drescher, D. G. (2009) J. Biol. Chem. 284, 3227-3238). We now show that Ca(2+)-dependent interaction of the organ of Corti HCN1 and protocadherin 15 CD3 is mediated by amino-terminal sequence specific to HCN1 and is not replicated by analogous specific peptides for HCN2 or HCN4 nor by amino-terminal sequence conserved across HCN isoforms utilized in channel formation. Furthermore, the HCN1-specific peptide binds both phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate and phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate but not phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate. Singly isolated cochlear inner and outer hair cells express HCN1 transcript, and HCN1 and HCN2 protein is immunolocalized to hair-cell stereocilia by both z-stack confocal and pre-embedding EM immunogold microscopy, with stereociliary tip-link and subcuticular plate sites. Quantitative PCR indicates HCN1/HCN2/HCN3/HCN4 = 9:9:1:89 in OC of the wild-type mouse, with HCN4 protein primarily attributable to inner sulcus cells. A mutant form of HCN1 mRNA and protein is expressed in the OC of an HCN1 mutant, corresponding to a full-length sequence with the in-frame deletion of pore-S6 domains, predicted by construct. The mutant transcript of HCN1 is ∼9-fold elevated relative to wild-type levels, possibly representing molecular compensation, with unsubstantial changes in HCN2, HCN3, and HCN4. Immunoprecipitation protocols indicate alternate interactions of full-length proteins; HCN1 can interact with protocadherin 15 CD3 and F-actin-binding filamin A forming a complex that does not include HCN2, or HCN1 can interact with HCN2 forming a complex without protocadherin 15 CD3 but including F-actin-binding fascin-2.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cyclic nucleotide-gated channel α-3 (CNGA3) interacts with stereocilia tip-link cadherin 23 + exon 68 or alternatively with myosin VIIa, two proteins required for hair cell mechanotransduction.J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 8;288(10):7215-29. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.443226. Epub 2013 Jan 17. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23329832 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium-dependent binding of HCN1 channel protein to hair cell stereociliary tip link protein protocadherin 15 CD3.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jan 30;284(5):3227-3238. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M806177200. Epub 2008 Nov 13. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19008224 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of the pacemaker channel HCN1 with filamin A.J Biol Chem. 2004 Oct 15;279(42):43847-53. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M401598200. Epub 2004 Jul 30. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15292205
-
HCN channelopathies: pathophysiology in genetic epilepsy and therapeutic implications.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Jan;165(1):49-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01507.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21615728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Contribution of HCN Channelopathies in Different Epileptic Syndromes, Mechanisms, Modulators, and Potential Treatment Targets: A Systematic Review.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 May 19;15:807202. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.807202. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35663267 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cyclophosphamide-induced HCN1 channel upregulation in interstitial Cajal-like cells leads to bladder hyperactivity in mice.Exp Mol Med. 2017 Apr 21;49(4):e319. doi: 10.1038/emm.2017.31. Exp Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28428632 Free PMC article.
-
HCN Channels Modulators: The Need for Selectivity.Curr Top Med Chem. 2016;16(16):1764-91. doi: 10.2174/1568026616999160315130832. Curr Top Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26975509 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An N-Terminal ER Export Signal Facilitates the Plasma Membrane Targeting of HCN1 Channels in Photoreceptors.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015 Jun;56(6):3514-21. doi: 10.1167/iovs.15-16902. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015. PMID: 26030105 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclic nucleotide-gated channel α-3 (CNGA3) interacts with stereocilia tip-link cadherin 23 + exon 68 or alternatively with myosin VIIa, two proteins required for hair cell mechanotransduction.J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 8;288(10):7215-29. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.443226. Epub 2013 Jan 17. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23329832 Free PMC article.
-
Association of SNPs in LCP1 and CTIF with hearing in 11 year old children: findings from the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC) birth cohort and the G-EAR consortium.BMC Med Genomics. 2015 Aug 12;8:48. doi: 10.1186/s12920-015-0112-2. BMC Med Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26264041 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cho W. J., Drescher M. J., Hatfield J. S., Bessert D. A., Skoff R. P., Drescher D. G. (2003) Hyperpolarization-activated, cyclic AMP-gated, HCN1-like cation channel. The primary, full-length HCN isoform expressed in a saccular hair-cell layer. Neuroscience 118, 525–534 - PubMed
-
- Seiler C., Finger-Baier K. C., Rinner O., Makhankov Y. V., Schwarz H., Neuhauss S. C., Nicolson T. (2005) Duplicated genes with split functions. Independent roles of protocadherin15 orthologues in zebrafish hearing and vision. Development 132, 615–623 - PubMed
-
- Kazmierczak P., Sakaguchi H., Tokita J., Wilson-Kubalek E. M., Milligan R. A., Müller U., Kachar B. (2007) Cadherin 23 and protocadherin 15 interact to form tip-link filaments in sensory hair cells. Nature 449, 87–91 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

