Characterization of conformation-dependent prion protein epitopes
- PMID: 22948149
- PMCID: PMC3481321
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.395921
Characterization of conformation-dependent prion protein epitopes
Abstract
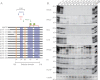
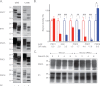
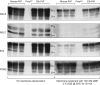
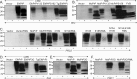
Whereas prion replication involves structural rearrangement of cellular prion protein (PrP(C)), the existence of conformational epitopes remains speculative and controversial, and PrP transformation is monitored by immunoblot detection of PrP(27-30), a protease-resistant counterpart of the pathogenic scrapie form (PrP(Sc)) of PrP. We now describe the involvement of specific amino acids in conformational determinants of novel monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) raised against randomly chimeric PrP. Epitope recognition of two mAbs depended on polymorphisms controlling disease susceptibility. Detection by one, referred to as PRC5, required alanine and asparagine at discontinuous mouse PrP residues 132 and 158, which acquire proximity when residues 126-218 form a structured globular domain. The discontinuous epitope of glycosylation-dependent mAb PRC7 also mapped within this domain at residues 154 and 185. In accordance with their conformational dependence, tertiary structure perturbations compromised recognition by PRC5, PRC7, as well as previously characterized mAbs whose epitopes also reside in the globular domain, whereas conformation-independent epitopes proximal or distal to this region were refractory to such destabilizing treatments. Our studies also address the paradox of how conformational epitopes remain functional following denaturing treatments and indicate that cellular PrP and PrP(27-30) both renature to a common structure that reconstitutes the globular domain.
Figures




References
-
- Stahl N., Borchelt D. R., Hsiao K., Prusiner S. B. (1987) Scrapie prion protein contains a phosphatidylinositol glycolipid. Cell 51, 229–240 - PubMed
-
- Riek R., Hornemann S., Wider G., Billeter M., Glockshuber R., Wüthrich K. (1996) NMR structure of the mouse prion protein domain PrP(121–231). Nature 382, 180–182 - PubMed
-
- Chen S. G., Teplow D. B., Parchi P., Teller J. K., Gambetti P., Autilio-Gambetti L. (1995) Truncated forms of the human prion protein in normal brain and in prion diseases. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 19173–19180 - PubMed
-
- Yadavalli R., Guttmann R. P., Seward T., Centers A. P., Williamson R. A., Telling G. C. (2004) Calpain-dependent endoproteolytic cleavage of PrPSc modulates scrapie prion propagation. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 21948–21956 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BBS/E/D/20251967/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BBS/E/D/20251968/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- P01 AI077774-015261/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- BBS/E/D/05241340/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 NS040334/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

