Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2), transforming growth factor-β, hyaluronan (HA), and receptor for HA-mediated motility (RHAMM) are required for surfactant protein A-stimulated macrophage chemotaxis
- PMID: 22948158
- PMCID: PMC3481337
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.360982
Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2), transforming growth factor-β, hyaluronan (HA), and receptor for HA-mediated motility (RHAMM) are required for surfactant protein A-stimulated macrophage chemotaxis
Abstract
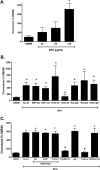
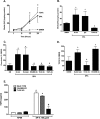
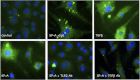
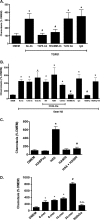
The innate immune system protects the host from bacterial and viral invasion. Surfactant protein A (SPA), a lung-specific collectin, stimulates macrophage chemotaxis. However, the mechanisms regulating this function are unknown. Hyaluronan (HA) and its receptors RHAMM (receptor for HA-mediated motility, CD168) and CD44 also regulate cell migration and inflammation. We therefore examined the role of HA, RHAMM, and CD44 in SPA-stimulated macrophage chemotaxis. Using antibody blockade and murine macrophages, SPA-stimulated macrophage chemotaxis was dependent on TLR2 but not the other SPA receptors examined. Anti-TLR2 blocked SPA-induced production of TGFβ. In turn, TGFβ1-stimulated chemotaxis was inhibited by HA-binding peptide and anti-RHAMM antibody but not anti-TLR2 antibody. Macrophages from TLR2(-/-) mice failed to migrate in response to SPA but responded normally to TGFβ1 and HA, effects that were blocked by anti-RHAMM antibody. Macrophages from WT and CD44(-/-) mice had similar responses to SPA, whereas those from RHAMM(-/-) mice had decreased chemotaxis to SPA, TGFβ1, and HA. In primary macrophages, SPA-stimulated TGFβ production was dependent on TLR2, JNK, and ERK but not p38. Pam3Cys, a specific TLR2 agonist, stimulated phosphorylation of JNK, ERK, and p38, but only JNK and ERK inhibition blocked Pam3Cys-stimulated chemotaxis. We have uncovered a novel pathway for SPA-stimulated macrophage chemotaxis where SPA stimulation via TLR2 drives JNK- and ERK-dependent TGFβ production. TGFβ1, in turn, stimulates macrophage chemotaxis in a RHAMM and HA-dependent manner. These findings are highly relevant to the regulation of innate immune responses by SPA with key roles for specific components of the extracellular matrix.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The Receptor for Hyaluronan-Mediated Motility (CD168) promotes inflammation and fibrosis after acute lung injury.Matrix Biol. 2019 May;78-79:255-271. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2018.08.002. Epub 2018 Aug 8. Matrix Biol. 2019. PMID: 30098420 Free PMC article.
-
Role of CD44 in Regulating TLR2 Activation of Human Macrophages and Downstream Expression of Proinflammatory Cytokines.J Immunol. 2018 Jan 15;200(2):758-767. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700713. Epub 2017 Dec 1. J Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29196459 Free PMC article.
-
Hyaluronic acid promotes angiogenesis by inducing RHAMM-TGFβ receptor interaction via CD44-PKCδ.Mol Cells. 2012 Jun;33(6):563-74. doi: 10.1007/s10059-012-2294-1. Epub 2012 May 18. Mol Cells. 2012. PMID: 22610405 Free PMC article.
-
Role of receptor for hyaluronan-mediated motility (RHAMM) in human head and neck cancers.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2014 Oct;140(10):1629-40. doi: 10.1007/s00432-014-1653-z. Epub 2014 Mar 28. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24676428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The roles of hyaluronan/RHAMM/CD44 and their respective interactions along the insidious pathways of fibrosarcoma progression.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:929531. doi: 10.1155/2013/929531. Epub 2013 Sep 5. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 24083250 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Modulators of inflammation in Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia.Semin Perinatol. 2018 Nov;42(7):459-470. doi: 10.1053/j.semperi.2018.09.009. Epub 2018 Oct 2. Semin Perinatol. 2018. PMID: 30446300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Annexin A4 is involved in proliferation, chemo-resistance and migration and invasion in ovarian clear cell adenocarcinoma cells.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 11;8(11):e80359. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080359. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24244679 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular Effects Mediated by HMMR and CD44.Mediators Inflamm. 2021 Jul 10;2021:4977209. doi: 10.1155/2021/4977209. eCollection 2021. Mediators Inflamm. 2021. PMID: 34335086 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyperoxia treatment of TREK-1/TREK-2/TRAAK-deficient mice is associated with a reduction in surfactant proteins.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017 Dec 1;313(6):L1030-L1046. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00121.2017. Epub 2017 Aug 24. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28839101 Free PMC article.
-
The Receptor for Hyaluronan-Mediated Motility (CD168) promotes inflammation and fibrosis after acute lung injury.Matrix Biol. 2019 May;78-79:255-271. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2018.08.002. Epub 2018 Aug 8. Matrix Biol. 2019. PMID: 30098420 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Waters P., Vaid M., Kishore U., Madan T. (2009) Lung surfactant proteins A and D as pattern recognition proteins. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 653, 74–97 - PubMed
-
- Wright J. R. (2005) Immunoregulatory functions of surfactant proteins. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 5, 58–68 - PubMed
-
- Wright J. R., Youmans D. C. (1993) Pulmonary surfactant protein A stimulates chemotaxis of alveolar macrophage. Am. J. Physiol. 264, L338–L344 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

