rpS6 Regulates blood-testis barrier dynamics by affecting F-actin organization and protein recruitment
- PMID: 22948214
- PMCID: PMC3512016
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2012-1665
rpS6 Regulates blood-testis barrier dynamics by affecting F-actin organization and protein recruitment
Abstract
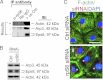
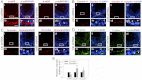
During spermatogenesis, preleptotene spermatocytes residing near the basement membrane of the seminiferous tubule must traverse the blood-testis barrier (BTB) at stage VIII-IX of the epithelial cycle to continue their development in the adluminal compartment. Unlike other blood-tissue barriers (e.g. the blood-brain barrier) that are created by the endothelial tight junction (TJ) barrier of capillaries, the BTB is created by specialized junctions between Sertoli cells in which TJ coexists with basal ectoplasmic specialization (basal ES, a testis-specific adherens junction). The basal ES is typified by the presence of tightly packed actin filament bundles sandwiched between cisternae of endoplasmic reticulum and the apposing plasma membranes of Sertoli cells. These actin filament bundles also confer unusual adhesive strength to the BTB. Yet the mechanisms by which these filamentous actin (F-actin) networks are regulated from the bundled to the debundled state to facilitate the transit of spermatocytes remain elusive. Herein, we provide evidence that ribosomal protein S6 (rpS6), the downstream signaling molecule of the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) pathway, is a major regulator of F-actin organization and adhesion protein recruitment at the BTB. rpS6 is restrictively and spatiotemporally activated at the BTB during the epithelial cycle. An activation of rpS6 led to a disruption of the Sertoli cell TJ barrier and BTB integrity. Its silencing in vitro or in vivo by using small interfering RNA duplexes or short hairpin RNA was found to promote the Sertoli cell TJ permeability barrier by the recruitment of adhesion proteins (e.g. claudin-11 and occludin) to the BTB. Thus, rpS6 in the mTORC1 pathway regulates BTB restructuring via its effects on the F-actin organization and protein recruitment at the BTB.
Figures
Similar articles
-
rpS6 regulates blood-testis barrier dynamics through Arp3-mediated actin microfilament organization in rat sertoli cells. An in vitro study.Endocrinology. 2015 May;156(5):1900-13. doi: 10.1210/en.2014-1791. Epub 2015 Feb 25. Endocrinology. 2015. PMID: 25714812 Free PMC article.
-
mTORC1/rpS6 signaling complex modifies BTB transport function: an in vivo study using the adjudin model.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2019 Jul 1;317(1):E121-E138. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00553.2018. Epub 2019 May 21. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2019. PMID: 31112404 Free PMC article.
-
Palladin is a regulator of actin filament bundles at the ectoplasmic specialization in adult rat testes.Endocrinology. 2013 May;154(5):1907-20. doi: 10.1210/en.2012-2269. Epub 2013 Apr 1. Endocrinology. 2013. PMID: 23546604 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin complex (mTOR) pathway modulates blood-testis barrier (BTB) function through F-actin organization and gap junction.Histol Histopathol. 2016 Sep;31(9):961-8. doi: 10.14670/HH-11-753. Epub 2016 Mar 9. Histol Histopathol. 2016. PMID: 26957088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Actin binding proteins in blood-testis barrier function.Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2015 Jun;22(3):238-47. doi: 10.1097/MED.0000000000000155. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2015. PMID: 25887390 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Focal adhesion kinase and actin regulatory/binding proteins that modulate F-actin organization at the tissue barrier: Lesson from the testis.Tissue Barriers. 2013 Apr 1;1(2):e24252. doi: 10.4161/tisb.24252. Tissue Barriers. 2013. PMID: 24665388 Free PMC article.
-
F5-Peptide and mTORC1/rpS6 Effectively Enhance BTB Transport Function in the Testis-Lesson From the Adjudin Model.Endocrinology. 2019 Aug 1;160(8):1832-1853. doi: 10.1210/en.2019-00308. Endocrinology. 2019. PMID: 31157869 Free PMC article.
-
Rictor/mTORC2 regulates blood-testis barrier dynamics via its effects on gap junction communications and actin filament network.FASEB J. 2013 Mar;27(3):1137-52. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-212977. Epub 2013 Jan 3. FASEB J. 2013. PMID: 23288930 Free PMC article.
-
The Non-hormonal Male Contraceptive Adjudin Exerts its Effects via MAPs and Signaling Proteins mTORC1/rpS6 and FAK-Y407.Endocrinology. 2021 Jan 1;162(1):bqaa196. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqaa196. Endocrinology. 2021. PMID: 33094326 Free PMC article.
-
The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway: How does it regulate development of Sertoli cells and spermatogenic cells?Histol Histopathol. 2022 Jul;37(7):621-636. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-457. Epub 2022 Apr 7. Histol Histopathol. 2022. PMID: 35388905 Review.
References
-
- Hertzog M, Milanesi F, Hazelwood L, Disanza A, Liu H, Perlade E, Malabarba MG, Pasqualato S, Maiolica A, Confalonieri S, Le Clainche C, Offenhauser N, Block J, Rottner K, Di Fiore PP, Carlier MF, Volkmann N, Hanein D, Scita G. 2010. Molecular basis for the dual function of Eps8 on actin dynamics: bundling and capping. PLoS Biol 8:e1000387. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

