Upregulation of TET1 and downregulation of APOBEC3A and APOBEC3C in the parietal cortex of psychotic patients
- PMID: 22948384
- PMCID: PMC3565208
- DOI: 10.1038/tp.2012.86
Upregulation of TET1 and downregulation of APOBEC3A and APOBEC3C in the parietal cortex of psychotic patients
Abstract
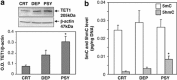
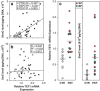
Increasing evidence suggests that epigenetic dysfunction may account for the alteration of gene transcription present in neuropsychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia (SZ), bipolar disorder (BP) and autism. Here, we studied the expression of the ten-eleven translocation (TET) gene family and activation-induced deaminase/apolipoprotein B mRNA-editing enzymes (AID/APOBEC) in the inferior parietal lobule (IPL) (BA39-40) and the cerebellum of psychotic (PSY) patients, depressed (DEP) patients and nonpsychiatric (CTR) subjects obtained from the Stanley Foundation Neuropathology Consortium Medical Research Institute. These two sets of enzymes have a critical role in the active DNA demethylation pathway. The results show that TET1, but not TET2 and TET3, mRNA and protein expression was increased (two- to threefold) in the IPL of the PSY patients compared with the CTR subjects. TET1 mRNA showed no change in the cerebellum. Consistent with the increase of TET1, the level of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) was elevated in the IPL of PSY patients but not in the other groups. Moreover, higher 5hmC levels were detected at the glutamic acid decarboxylase67 (GAD67) promoter only in the PSY group. This increase was inversely related to the decrease of GAD67 mRNA expression. Of 11 DNA deaminases measured, APOBEC3A mRNA was significantly decreased in the PSY and DEP patients, while APOBEC3C was decreased only in PSY patients. The other APOBEC mRNA studied failed to change. Increased TET1 and decreased APOBEC3A and APOBEC3C found in this study highlight the possible role of altered DNA demethylation mechanisms in the pathophysiology of psychosis.
Figures
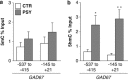
 ) compared with nonpsychiatric (CTR) subjects (□) at both regions of the GAD67 promoter examined. *P<0.05 vs CTR; **P<0.01 vs CTR.
) compared with nonpsychiatric (CTR) subjects (□) at both regions of the GAD67 promoter examined. *P<0.05 vs CTR; **P<0.01 vs CTR.Similar articles
-
TET enzymes are successively expressed during human spermatogenesis and their expression level is pivotal for male fertility.Hum Reprod. 2016 Jul;31(7):1411-24. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dew096. Epub 2016 May 1. Hum Reprod. 2016. PMID: 27141042
-
DNA-methyltransferase1 (DNMT1) binding to CpG rich GABAergic and BDNF promoters is increased in the brain of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder patients.Schizophr Res. 2015 Sep;167(1-3):35-41. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2014.10.030. Epub 2014 Dec 2. Schizophr Res. 2015. PMID: 25476119 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristic profiles of DNA epigenetic modifications in colon cancer and its predisposing conditions-benign adenomas and inflammatory bowel disease.Clin Epigenetics. 2018 May 30;10:72. doi: 10.1186/s13148-018-0505-0. eCollection 2018. Clin Epigenetics. 2018. PMID: 29875879 Free PMC article.
-
Role of ten-eleven translocation proteins and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cell Prolif. 2019 Jul;52(4):e12626. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12626. Epub 2019 Apr 29. Cell Prolif. 2019. PMID: 31033072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple Functions of Ten-eleven Translocation 1 during Tumorigenesis.Chin Med J (Engl). 2016 Jul 20;129(14):1744-51. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.185873. Chin Med J (Engl). 2016. PMID: 27411465 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic mechanisms in schizophrenia.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2015 Jul;118(1-2):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2015.04.008. Epub 2015 May 7. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25958205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Insights into TETs in Psychiatric Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 28;23(9):4909. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094909. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Active DNA demethylation in post-mitotic neurons: a reason for optimism.Neuropharmacology. 2013 Dec;75:233-45. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.07.036. Epub 2013 Aug 16. Neuropharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23958448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gestational stress induces depressive-like and anxiety-like phenotypes through epigenetic regulation of BDNF expression in offspring hippocampus.Epigenetics. 2016;11(2):150-62. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2016.1146850. Epub 2016 Feb 18. Epigenetics. 2016. PMID: 26890656 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of DDAH1 and DDAH2 Contributions to Psychiatric Disorders via In Silico Methods.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 7;23(19):11902. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911902. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36233204 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goll MG, Bestor TH. Eukaryotic cytosine methyltransferases. Annu Rev Biochem. 2005;74:481–514. - PubMed
-
- Abdolmaleky HM, Cheng KH, Russo A, Smith CL, Faraone SV, Wilcox M, et al. Hypermethylation of the reelin (RELN) promoter in the brain of schizophrenic patients: a preliminary report. Am J Med Genet B. 2005;134B:60–66. - PubMed
-
- Akbarian S. Epigenetics of schizophrenia. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2010;4:611–628. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

