Characterization of Highper, an ENU-induced mouse mutant with abnormal psychostimulant and stress responses
- PMID: 22948668
- PMCID: PMC3536991
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-012-2827-5
Characterization of Highper, an ENU-induced mouse mutant with abnormal psychostimulant and stress responses
Abstract
Rationale: Chemical mutagenesis in the mouse is a forward genetics approach that introduces random mutations into the genome, thereby providing an opportunity to annotate gene function and characterize phenotypes that have not been previously linked to a given gene.
Objectives: We report on the behavioral characterization of Highper, an N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea (ENU)-induced mutant mouse line.
Methods: Highper and B6 control mice were assessed for locomotor activity in the open field and home cage environments. Basal and acute restraint stress-induced corticosterone levels were measured. Mice were tested for locomotor response to cocaine (5, 20, 30, and 45 mg/kg), methylphenidate (30 mg/kg), and ethanol (0.75, 1.25, and 1.75 g/kg). The rewarding and reinforcing effects of cocaine were assessed using conditioned place preference and self-administration paradigms.
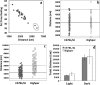
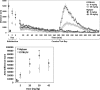
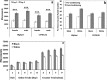
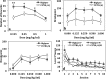
Results: Highper mice are hyperactive during behavioral tests but show normal home cage locomotor behavior. Highper mice also exhibit a twofold increase in locomotor response to cocaine, methylphenidate, and ethanol and prolonged activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in response to acute stress. Highper mice are more sensitive to the rewarding and reinforcing effects of cocaine, although place preference in Highper mice appears to be significantly influenced by the environment in which the drug is administered.
Conclusions: Altogether, our findings indicate that Highper mice may provide important insights into the genetic, molecular, and biological mechanisms underlying stress and the drug reward pathway.
Figures
References
-
- Alsio J, Nordenankar K, Arvidsson E, Birgner C, Mahmoudi S, Halbout B, Smith C, Fortin GM, Olson L, Descarries L, Trudeau LE, Kullander K, Levesque D, Wallen-Mackenzie A. Enhanced sucrose and cocaine self-administration and cue-induced drug seeking after loss of VGLUT2 in midbrain dopamine neurons in mice. J Neurosci. 2011;31:12593–12603. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2397-11.2011. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bierut LJ, Dinwiddie SH, Begleiter H, Crowe RR, Hesselbrock V, Nurnberger JI, Jr, Porjesz B, Schuckit MA, Reich T. Familial transmission of substance dependence: alcohol, marijuana, cocaine, and habitual smoking: a report from the Collaborative Study on the Genetics of Alcoholism. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1998;55:982–988. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.55.11.982. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Borowsky B, Kuhn CM. Monoamine mediation of cocaine-induced hypothalamo–pituitary–adrenal activation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991;256:204–210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

