Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MEK/ERK) inhibition sensitizes cancer cells to centromere-associated protein E inhibition
- PMID: 22948716
- PMCID: PMC4706358
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.27781
Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MEK/ERK) inhibition sensitizes cancer cells to centromere-associated protein E inhibition
Abstract
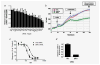
Inhibition of centromere-associated protein-E (CENP-E) has demonstrated preclinical anti-tumor activity in a number of tumor types including neuroblastoma. A potent small molecule inhibitor of the kinesin motor activity of CENP-E has recently been developed (GSK923295). To identify an effective drug combination strategy for GSK923295 in neuroblastoma, we performed a screen of siRNAs targeting a prioritized set of genes that function in therapeutically tractable signaling pathways. We found that siRNAs targeted to extracellular signal-related kinase 1 (ERK1) significantly sensitized neuroblastoma cells to GSK923295-induced growth inhibition (p = 0.01). Inhibition of ERK1 activity using pharmacologic inhibitors of mitogen-activated ERK kinase (MEK1/2) showed significant synergistic growth inhibitory activity when combined with GSK923295 in neuroblastoma, lung, pancreatic and colon carcinoma cell lines. Synergistic growth inhibitory activity of combined MEK/ERK and CENP-E inhibition was a result of increased mitotic arrest and apoptosis. There was a significant correlation between ERK1/2 phosphorylation status in neuroblastoma cell lines and GSK923295 growth inhibitory activity (r = 0.823, p = 0.0006). Consistent with this result we found that lung cancer cell lines harboring RAS mutations, which leads to oncogenic activation of MEK/ERK signaling, were significantly more resistant than cell lines with wild-type RAS to GSK923295-induced growth inhibition (p = 0.047). Here we have identified (MEK/ERK) activity as a potential biomarker of relative GSK923295 sensitivity and have shown the synergistic effect of combinatorial MEK/ERK pathway and CENP-E inhibition across different cancer cell types including neuroblastoma.
Copyright © 2012 UICC.
Figures
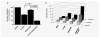


References
-
- Wood KW, Chua P, Sutton D, et al. Centromere-associated protein E: a motor that puts the brakes on the mitotic checkpoint. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:7588–92. - PubMed
-
- Mao Y, Abrieu A, Cleveland DW. Activating and silencing the mitotic checkpoint through CENP-E-dependent activation/inactivation of BubR1. Cell. 2003;114:87–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

