Comparison of fluconazole renal penetration levels in healthy and Candida albicans-infected Wistar rats
- PMID: 22948869
- PMCID: PMC3486536
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01323-12
Comparison of fluconazole renal penetration levels in healthy and Candida albicans-infected Wistar rats
Abstract
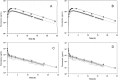
The aims of this study were to evaluate free levels of fluconazole (FCZ) in the kidneys of healthy and Candida albicans-infected Wistar rats using microdialysis and to establish the relationship between free renal and total plasma levels under both conditions. Microdialysis recovery rates were determined in vitro by dialysis, and retrodialysis recovery rates were determined in vivo by retrodialysis. The recovery rate was around 50%, independent of the method, drug concentration, or condition (in vitro or in vivo) used. FCZ kidney penetration in healthy and infected rats was investigated after the administration of 10 mg/kg of body weight intravenously (i.v.) or 50 mg/kg orally (n = 6/group) and blood and microdialysate sample harvesting at predetermined time points up to 24 and 18 h, respectively. There were no statistical differences between the area under the free concentration-time curve (AUC(0-∞)) values in plasma and in tissue for either healthy or infected groups for the same dose regimen investigated. The antifungal tissue penetrations were similar for both doses and under all conditions investigated (ranging from 0.77 to 0.84). The unbound fraction of FCZ was concentration independent (86.0% ± 2.0%), allowing the prediction of free renal levels using pharmacokinetic parameters obtained from total plasma fitting. The results showed that free renal and free plasma levels are similar in healthy and systemically C. albicans-infected rats. Therefore, free plasma levels are a good surrogate to estimate free FCZ renal concentrations in systemic candidiasis and can be used to optimize dosing regimens for this drug.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Free renal levels of voriconazole determined by microdialysis in healthy and Candida sp.-infected Wistar rats.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2009 Feb;33(2):154-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2008.08.020. Epub 2008 Nov 17. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2009. PMID: 19010646
-
Characterization and quantitation of the pharmacodynamics of fluconazole in a neutropenic murine disseminated candidiasis infection model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999 Sep;43(9):2116-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.43.9.2116. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999. PMID: 10471550 Free PMC article.
-
In Vivo Microdialysis To Determine Subcutaneous Interstitial Fluid Penetration and Pharmacokinetics of Fluconazole in Intensive Care Unit Patients with Sepsis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Nov 23;60(2):827-32. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02461-15. Print 2016 Feb. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 26596947 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetic evaluation of fluconazole in critically ill patients.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2011 Nov;7(11):1431-40. doi: 10.1517/17425255.2011.615309. Epub 2011 Sep 2. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2011. PMID: 21883033 Review.
-
Candida albicans targets that potentially synergize with fluconazole.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2021 May;47(3):323-337. doi: 10.1080/1040841X.2021.1884641. Epub 2021 Feb 15. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33587857 Review.
Cited by
-
Simultaneous Semimechanistic Population Analyses of Levofloxacin in Plasma, Lung, and Prostate To Describe the Influence of Efflux Transporters on Drug Distribution following Intravenous and Intratracheal Administration.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Nov 30;60(2):946-54. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02317-15. Print 2016 Feb. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 26621623 Free PMC article.
-
Amphotericin B tissue penetration and pharmacokinetics in healthy and Candida albicans-infected rats: insights from microdialysis and population modeling.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 10;15:1515462. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1515462. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39867661 Free PMC article.
-
Population pharmacokinetic modeling of the unbound levofloxacin concentrations in rat plasma and prostate tissue measured by microdialysis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58(2):678-86. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01884-13. Epub 2013 Nov 11. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014. PMID: 24217697 Free PMC article.
-
Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling to Describe the Total Plasma and Free Brain Levels of Fluconazole in Healthy and Cryptococcus neoformans Infected Rats: How Does the Infection Impact the Drug's Levels on Biophase?Pharm Res. 2018 Apr 27;35(7):132. doi: 10.1007/s11095-018-2402-9. Pharm Res. 2018. PMID: 29704215
-
Utility of Microdialysis in Infectious Disease Drug Development and Dose Optimization.AAPS J. 2017 Mar;19(2):334-342. doi: 10.1208/s12248-016-0020-1. Epub 2016 Dec 9. AAPS J. 2017. PMID: 27943149 Review.
References
-
- Andes D. 2006. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of antifungals. Infect. Dis. Clin. North Am. 20:679–697 - PubMed
-
- Araujo BV, Silva CF, Haas SE, Dalla Costa T. 2008. Microdialysis as a tool to determine the free kidney levels of voriconazole in rodents: a model to study the technique feasibility for a moderately lipophilic drug. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 47:876–881 - PubMed
-
- Araujo BV, Silva CF, Haas SE, Dalla Costa T. 2009. Free renal levels of voriconazole determined by microdialysis in healthy and Candida sp.-infected Wistar rats. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 33:154–159 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

