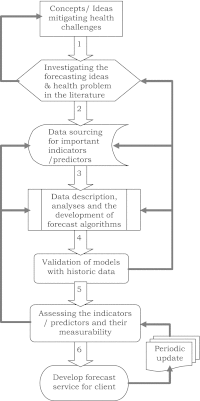
An overview of health forecasting
- PMID: 22949173
- PMCID: PMC3541816
- DOI: 10.1007/s12199-012-0294-6
An overview of health forecasting
Abstract
Health forecasting is a novel area of forecasting, and a valuable tool for predicting future health events or situations such as demands for health services and healthcare needs. It facilitates preventive medicine and health care intervention strategies, by pre-informing health service providers to take appropriate mitigating actions to minimize risks and manage demand. Health forecasting requires reliable data, information and appropriate analytical tools for the prediction of specific health conditions or situations. There is no single approach to health forecasting, and so various methods have often been adopted to forecast aggregate or specific health conditions. Meanwhile, there are no defined health forecasting horizons (time frames) to match the choices of health forecasting methods/approaches that are often applied. The key principles of health forecasting have not also been adequately described to guide the process. This paper provides a brief introduction and theoretical analysis of health forecasting. It describes the key issues that are important for health forecasting, including: definitions, principles of health forecasting, and the properties of health data, which influence the choices of health forecasting methods. Other matters related to the value of health forecasting, and the general challenges associated with developing and using health forecasting services are discussed. This overview is a stimulus for further discussions on standardizing health forecasting approaches and methods that will facilitate health care and health services delivery.
Figures
References
-
- Armstrong JS. Principles of forecasting: a handbook for researchers and practitioners. Norwell: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 2001.
-
- Lewis JB, McGrath RJ, Seidel LF. Essentials of applied quantitative methods for health services managers. Sudbury: Jones and Bartlett Publishers, LLC.; 2011.
-
- Chadwick J, Mann WN. Medicine. In: Lloyd GER, editor. Hippocratic writings. England: Penguin Group; 1978. p. 170–171.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical