Purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of crotamine, a myotoxic polypeptide from the Brazilian snake Crotalus durissus terrificus
- PMID: 22949192
- PMCID: PMC3433195
- DOI: 10.1107/S1744309112032721
Purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of crotamine, a myotoxic polypeptide from the Brazilian snake Crotalus durissus terrificus
Abstract
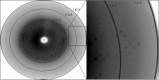
Crotamine, a highly basic myotoxic polypeptide (molecular mass 4881 Da) isolated from the venom of the Brazilian rattlesnake Crotalus durissus terrificus, causes skeletal muscle contraction and spasms, affects the functioning of voltage-sensitive sodium channels by inducing sodium influx and possesses antitumour activity, suggesting potential pharmaceutical applications. Crotamine was purified from C. durissus terrificus venom; the crystals diffracted to 1.9 Å resolution and belonged to the orthorhombic space group I2(1)2(1)2(1) or I222, with unit-cell parameters a = 67.75, b = 74.4, c = 81.01 Å. The self-rotation function indicated that the asymmetric unit contained three molecules. However, structure determination by molecular replacement using NMR-determined coordinates was unsuccessful and a search for potential derivatives has been initiated.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structure of the polypeptide crotamine from the Brazilian rattlesnake Crotalus durissus terrificus.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2013 Oct;69(Pt 10):1958-64. doi: 10.1107/S0907444913018003. Epub 2013 Sep 20. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2013. PMID: 24100315 Free PMC article.
-
Snake venomics and antivenomics of Crotalus durissus subspecies from Brazil: assessment of geographic variation and its implication on snakebite management.J Proteomics. 2010 Aug 5;73(9):1758-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2010.06.001. Epub 2010 Jun 11. J Proteomics. 2010. PMID: 20542151
-
Initial structural analysis of an alpha4beta4 C-type lectin from the venom of Crotalus durissus terrificus.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2003 Oct;59(Pt 10):1813-5. doi: 10.1107/s0907444903016202. Epub 2003 Sep 19. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2003. PMID: 14501123
-
New view on crotamine, a small basic polypeptide myotoxin from South American rattlesnake venom.Toxicon. 2005 Sep 15;46(4):363-70. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2005.06.009. Toxicon. 2005. PMID: 16115660 Review.
-
Literature Review on Crotalus durissus terrificus Toxins: From a Perspective of Structural Biology and Therapeutic Applications.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2023;24(7):536-550. doi: 10.2174/1389203724666230607105355. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2023. PMID: 37287292 Review.
Cited by
-
Neurotoxicity in snakebite--the limits of our knowledge.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013 Oct 10;7(10):e2302. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002302. eCollection 2013. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013. PMID: 24130909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial peptides in reptiles.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2014 Jun 10;7(6):723-53. doi: 10.3390/ph7060723. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2014. PMID: 24918867 Free PMC article.
-
Biological and Medical Aspects Related to South American Rattlesnake Crotalus durissus (Linnaeus, 1758): A View from Colombia.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Dec 15;14(12):875. doi: 10.3390/toxins14120875. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36548772 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure of the polypeptide crotamine from the Brazilian rattlesnake Crotalus durissus terrificus.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2013 Oct;69(Pt 10):1958-64. doi: 10.1107/S0907444913018003. Epub 2013 Sep 20. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2013. PMID: 24100315 Free PMC article.
-
Design of D-Amino Acids SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors Using the Cationic Peptide from Rattlesnake Venom as a Scaffold.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Apr 27;15(5):540. doi: 10.3390/ph15050540. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35631367 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boni-Mitake, M., Costa, H., Spencer, P. J., Vassilieff, V. S. & Rogero, J. R. (2001). Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 34, 1531–1538. - PubMed
-
- Fadel, V., Bettendorff, P., Herrmann, T., de Azevedo, W. F., Oliveira, E. B., Yamane, T. & Wüthrich, K. (2005). Toxicon, 46, 759–767. - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Caballero, A. et al. (2011). Cryst. Growth Des. 11, 2112–2121.
-
- Giglio, J. R. (1975). Anal. Biochem. 69, 207–221. - PubMed
-
- Gonçalves, J. M. & Polson, A. (1947). Arch. Biochem. 13, 253–259. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

