Purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of crotamine, a myotoxic polypeptide from the Brazilian snake Crotalus durissus terrificus
- PMID: 22949192
- PMCID: PMC3433195
- DOI: 10.1107/S1744309112032721
Purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of crotamine, a myotoxic polypeptide from the Brazilian snake Crotalus durissus terrificus
Abstract
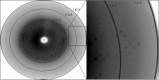
Crotamine, a highly basic myotoxic polypeptide (molecular mass 4881 Da) isolated from the venom of the Brazilian rattlesnake Crotalus durissus terrificus, causes skeletal muscle contraction and spasms, affects the functioning of voltage-sensitive sodium channels by inducing sodium influx and possesses antitumour activity, suggesting potential pharmaceutical applications. Crotamine was purified from C. durissus terrificus venom; the crystals diffracted to 1.9 Å resolution and belonged to the orthorhombic space group I2(1)2(1)2(1) or I222, with unit-cell parameters a = 67.75, b = 74.4, c = 81.01 Å. The self-rotation function indicated that the asymmetric unit contained three molecules. However, structure determination by molecular replacement using NMR-determined coordinates was unsuccessful and a search for potential derivatives has been initiated.
Figures


References
-
- Boni-Mitake, M., Costa, H., Spencer, P. J., Vassilieff, V. S. & Rogero, J. R. (2001). Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 34, 1531–1538. - PubMed
-
- Fadel, V., Bettendorff, P., Herrmann, T., de Azevedo, W. F., Oliveira, E. B., Yamane, T. & Wüthrich, K. (2005). Toxicon, 46, 759–767. - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Caballero, A. et al. (2011). Cryst. Growth Des. 11, 2112–2121.
-
- Giglio, J. R. (1975). Anal. Biochem. 69, 207–221. - PubMed
-
- Gonçalves, J. M. & Polson, A. (1947). Arch. Biochem. 13, 253–259. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

