Crystallization and preliminary X-ray characterization of a type III cohesin-dockerin complex from the cellulosome system of Ruminococcus flavefaciens
- PMID: 22949209
- PMCID: PMC3433212
- DOI: 10.1107/S1744309112033088
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray characterization of a type III cohesin-dockerin complex from the cellulosome system of Ruminococcus flavefaciens
Abstract
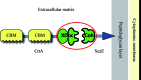
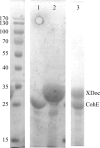
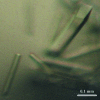
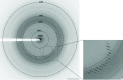
In Ruminococcus flavefaciens, a predominant fibre-degrading bacterium found in ruminants, cellulosomal proteins are anchored to the bacterial cell wall through a relatively small ScaE scaffoldin which includes a single type III cohesin. The cotton-binding protein CttA consists of two cellulose-binding modules and a C-terminal modular pair (XDoc) comprising an X-module and a contiguous dockerin, which exhibits high affinity towards the ScaE cohesin. Seleno-L-methionine-labelled derivatives of the ScaE cohesin module and the XDoc from CttA have been expressed, copurified and cocrystallized. The crystals belonged to the tetragonal space group P4(3)2(1)2, with unit-cell parameters a = b = 78.7, c = 203.4 Å, and the unit cell contains a single cohesin-XDoc complex in the asymmetric unit. The diffraction data were phased to 2.0 Å resolution using the anomalous signal of the Se atoms.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Atypical cohesin-dockerin complex responsible for cell surface attachment of cellulosomal components: binding fidelity, promiscuity, and structural buttresses.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jun 7;288(23):16827-16838. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.466672. Epub 2013 Apr 11. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23580648 Free PMC article.
-
Expression, purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of CttA, a putative cellulose-binding protein from Ruminococcus flavefaciens.Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2015 Jun;71(Pt 6):784-9. doi: 10.1107/S2053230X15008249. Epub 2015 May 22. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2015. PMID: 26057813 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression, crystallization and preliminary X-ray characterization of Ruminococcus flavefaciens scaffoldin C cohesin in complex with a dockerin from an uncharacterized CBM-containing protein.Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2014 Aug;70(Pt 8):1061-4. doi: 10.1107/S2053230X14012667. Epub 2014 Jul 23. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2014. PMID: 25084382 Free PMC article.
-
Single versus dual-binding conformations in cellulosomal cohesin-dockerin complexes.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2016 Oct;40:89-96. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2016.08.002. Epub 2016 Aug 28. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2016. PMID: 27579515 Review.
-
Insights into cellulosome assembly and dynamics: from dissection to reconstruction of the supramolecular enzyme complex.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2013 Oct;23(5):686-94. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2013.09.002. Epub 2013 Sep 27. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2013. PMID: 24080387 Review.
Cited by
-
Atypical cohesin-dockerin complex responsible for cell surface attachment of cellulosomal components: binding fidelity, promiscuity, and structural buttresses.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jun 7;288(23):16827-16838. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.466672. Epub 2013 Apr 11. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23580648 Free PMC article.
-
A genomic analysis reveals the diversity of cellulosome displaying bacteria.Front Microbiol. 2024 Oct 30;15:1473396. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1473396. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39539715 Free PMC article.
-
Complexity of the Ruminococcus flavefaciens FD-1 cellulosome reflects an expansion of family-related protein-protein interactions.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 10;7:42355. doi: 10.1038/srep42355. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28186207 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams, J. J., Currie, M. A., Ali, S., Bayer, E. A., Jia, Z. & Smith, S. P. (2010). J. Mol. Biol. 396, 833–839. - PubMed
-
- Adams, P. D. et al. (2011). Methods, 55, 94–106. - PubMed
-
- Alber, O., Noach, I., Rincon, M. T., Flint, H. J., Shimon, L. J. W., Lamed, R., Frolow, F. & Bayer, E. A. (2009). Proteins, 77, 699–709. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

