Impaired hepatitis C virus (HCV)-specific interferon-γ responses in individuals with HIV who acquire HCV infection: correlation with CD4(+) T-cell counts
- PMID: 22949308
- PMCID: PMC3475632
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jis544
Impaired hepatitis C virus (HCV)-specific interferon-γ responses in individuals with HIV who acquire HCV infection: correlation with CD4(+) T-cell counts
Abstract
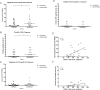
Studies examining the effect of coinfection with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) on the HCV-specific immune response in acute HCV infection are limited. This study directly compared acute HCV-specific T-cell responses and cytokine profiles between 20 HIV/HCV-coinfected and 20 HCV-monoinfected subjects, enrolled in the Australian Trial in Acute Hepatitis C (ATAHC), using HCV peptide enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISPOT) and multiplex in vitro cytokine production assays. HIV/HCV coinfection had a detrimental effect on the HCV-specific cytokine production in acute HCV infection, particularly on HCV-specific interferon γ (IFN-γ) production (magnitude P = .004; breadth P = .046), which correlated with peripheral CD4(+) T-cell counts (ρ = 0.605; P = .005) but not with detectable HIV viremia (ρ = 0.152; P = .534).
Figures

References
-
- Sulkowski MS, Thomas DL. Hepatitis C in the HIV-infected person. Ann Intern Med. 2003;138:197–207. - PubMed
-
- van den Berg CHSB, Ruys TA, Nanlohy NM, et al. Comprehensive longitudinal analysis of hepatitis C virus (HCV)-specific T cell responses during acute HCV infection in the presence of existing HIV-1 infection. J Viral Hepat. 2009;16:239–48. - PubMed
-
- Schnuriger A, Dominguez S, Guiguet M, et al. Acute hepatitis C in HIV-infected patients: rare spontaneous clearance correlates with weak memory CD4 T-cell responses to hepatitis C virus. AIDS. 2009;23:2079–89. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

