Risk of heart failure in breast cancer patients after anthracycline and trastuzumab treatment: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 22949432
- PMCID: PMC3433392
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djs317
Risk of heart failure in breast cancer patients after anthracycline and trastuzumab treatment: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Clinical trials demonstrated that women treated for breast cancer with anthracycline or trastuzumab are at increased risk for heart failure and/or cardiomyopathy (HF/CM), but the generalizability of these findings is unknown. We estimated real-world adjuvant anthracycline and trastuzumab use and their associations with incident HF/CM.
Methods: We conducted a population-based, retrospective cohort study of 12,500 women diagnosed with incident, invasive breast cancer from January 1, 1999 through December 31, 2007, at eight integrated Cancer Research Network health systems. Using administrative procedure and pharmacy codes, we identified anthracycline, trastuzumab, and other chemotherapy use. We identified incident HF/CM following chemotherapy initiation and assessed risk of HF/CM with time-varying chemotherapy exposures vs no chemotherapy. Multivariable Cox proportional hazards regression models were used to estimate hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) with adjustment for age at diagnosis, stage, Cancer Research Network site, year of diagnosis, radiation therapy, and comorbidities.
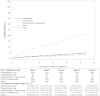
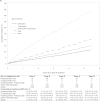
Results: Among 12 500 women (mean age = 60 years, range = 22-99 years), 29.6% received anthracycline alone, 0.9% received trastuzumab alone, 3.5% received anthracycline plus trastuzumab, 19.5% received other chemotherapy, and 46.5% received no chemotherapy. Anthracycline and trastuzumab recipients were younger, with fewer comorbidities than recipients of other chemotherapy or none. Compared with no chemotherapy, the risk of HF/CM was higher in patients treated with anthracycline alone (adjusted HR = 1.40, 95% CI = 1.11 to 1.76), although the increased risk was similar to other chemotherapy (adjusted HR = 1.49, 95% CI = 1.25 to 1.77); the risk was highly increased in patients treated with trastuzumab alone (adjusted HR = 4.12, 95% CI = 2.30 to 7.42) or anthracycline plus trastuzumab (adjusted HR = 7.19, 95% CI = 5.00 to 10.35).
Conclusions: Anthracycline and trastuzumab were primarily used in younger, healthier women and associated with increased HF/CM risk compared with no chemotherapy. This population-based observational study complements findings from clinical trials on cancer treatment safety.
Figures



Comment in
-
Trastuzumab and congestive heart failure: what can we learn from use in the community?J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012 Sep 5;104(17):1269-70. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djs342. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012. PMID: 22949431 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- American Cancer Society Cancer Facts & Figures 2011 Atlanta, GA: American Cancer Society; 2011.
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN). NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology—v.2.2011, Breast Cancer Fort Washington, PA: NCCN; 2011. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/breast.pdf Accessed April 20, 2011.
-
- Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, Levin WJ, Ullrich A, McGuire WL. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene Science. 1987. 235(4785 177–182 - PubMed
-
- Owens MA, Horten BC, Da Silva MM. HER2 amplification ratios by fluorescence in situ hybridization and correlation with immunohistochemistry in a cohort of 6556 breast cancer tissues Clin Breast Cancer. 2004. 5(1 63–69 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

