Television watching, leisure time physical activity, and the genetic predisposition in relation to body mass index in women and men
- PMID: 22949498
- PMCID: PMC3667660
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.098061
Television watching, leisure time physical activity, and the genetic predisposition in relation to body mass index in women and men
Abstract
Background: Previous studies on gene-lifestyle interaction and obesity have focused mostly on the FTO gene and physical activity, whereas little attention has been paid to sedentary behavior as indicated by television (TV) watching.
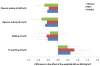
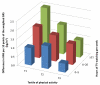
Methods and results: We analyzed interactions between TV watching, leisure time physical activity, and genetic predisposition in relation to body mass index (BMI) in 7740 women and 4564 men from 2 prospective cohorts: The Nurses' Health Study and the Health Professionals Follow-up Study. Data on physical activity and TV watching were collected 2 years before assessment of BMI. A weighted genetic risk score was calculated on the basis of 32 established BMI-associated variants. In both women and men, the genetic associations with BMI strengthened with increased hours of TV watching. An increment of 10 points in the weighted genetic risk score was associated with 0.8 (SE, 0.4), 0.8 (SE, 0.2), 1.4 (SE, 0.2), 1.5 (SE, 0.2), and 3.4 (SE, 1.0) kg/m(2) higher BMI across the 5 categories of TV watching (0-1, 2-5, 6-20, 21-40, and >40 h/wk; P for interaction=0.001). In contrast, the genetic association with BMI weakened with increased levels of physical activity. An increment of 10 points in the weighted genetic risk score was associated with 1.5 (SE, 0.2), 1.3 (SE, 0.2), 1.2 (SE, 0.2), 1.2 (SE, 0.2), and 0.8 (SE, 0.2) kg/m(2) higher BMI across the quintiles of physical activity. The interactions of TV watching and physical activity with genetic predisposition in relation to BMI were independent of each other.
Conclusions: A sedentary lifestyle, indicated by prolonged TV watching, may accentuate the predisposition to elevated adiposity, whereas greater leisure time physical activity may attenuate the genetic association.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of leisure time physical activity, watching television, obesity & lipid profile among sedentary low-income south Indian population.East Afr J Public Health. 2010 Sep;7(3):225-8. doi: 10.4314/eajph.v7i3.64732. East Afr J Public Health. 2010. PMID: 21516959
-
Television watching and other sedentary behaviors in relation to risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus in women.JAMA. 2003 Apr 9;289(14):1785-91. doi: 10.1001/jama.289.14.1785. JAMA. 2003. PMID: 12684356
-
Influence of leisure time physical activity and television watching on atherosclerosis risk factors in the NHLBI Family Heart Study.Atherosclerosis. 2000 Dec;153(2):433-43. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9150(00)00426-3. Atherosclerosis. 2000. PMID: 11164433 Clinical Trial.
-
Sedentary lifestyle and risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes.Lipids. 2003 Feb;38(2):103-8. doi: 10.1007/s11745-003-1038-4. Lipids. 2003. PMID: 12733740 Review.
-
How is television time linked to cardiometabolic health in adults? A critical systematic review of the evidence for an effect of watching television on eating, movement, affect and sleep.BMJ Open. 2021 May 5;11(5):e040739. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-040739. BMJ Open. 2021. PMID: 33952532 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Sleep patterns, genetic susceptibility, and incident cardiovascular disease: a prospective study of 385 292 UK biobank participants.Eur Heart J. 2020 Mar 14;41(11):1182-1189. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz849. Eur Heart J. 2020. PMID: 31848595 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Gene-Environment Interaction on Obesity among Chinese Adults Born in the Early 1960s.Genes (Basel). 2021 Feb 13;12(2):270. doi: 10.3390/genes12020270. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33668547 Free PMC article.
-
Habitual consumption of long-chain n-3 PUFAs and fish attenuates genetically associated long-term weight gain.Am J Clin Nutr. 2019 Mar 1;109(3):665-673. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqy238. Am J Clin Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30629107 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Conceptual heuristic models of the interrelationships between obesity and the occupational environment.Scand J Work Environ Health. 2013 May 1;39(3):221-32. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.3363. Epub 2013 Apr 15. Scand J Work Environ Health. 2013. PMID: 23588858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene-Diet Interactions in Complex Disease: Current Findings and Relevance for Public Health.Curr Nutr Rep. 2012 Dec 1;1(4):222-227. doi: 10.1007/s13668-012-0029-8. Curr Nutr Rep. 2012. PMID: 23139897 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Finucane MM, Stevens GA, Cowan MJ, Danaei G, Lin JK, Paciorek CJ, Singh GM, Gutierrez HR, Lu Y, Bahalim AN, Farzadfar F, Riley LM, Ezzati M. National, regional, and global trends in body-mass index since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 960 country-years and 9.1 million participants. Lancet. 2011;377:557–567. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Speliotes EK, Willer CJ, Berndt SI, Monda KL, Thorleifsson G, Jackson AU, Allen HL, Lindgren CM, Luan Ja, Magi R, Randall JC, Vedantam S, Winkler TW, Qi L, Workalemahu T, Heid IM, Steinthorsdottir V, Stringham HM, Weedon MN, Wheeler E, Wood AR, Ferreira T, Weyant RJ, Segre AV, Estrada K, Liang L, Nemesh J, Park J-H, Gustafsson S, Kilpelainen TO, Yang J, Bouatia-Naji N, Esko T, Feitosa MF, Kutalik Z, Mangino M, Raychaudhuri S, Scherag A, Smith AV, Welch R, Zhao JH, Aben KK, Absher DM, Amin N, Dixon AL, Fisher E, Glazer NL, Goddard ME, Heard-Costa NL, Hoesel V, Hottenga J-J, Johansson A, Johnson T, Ketkar S, Lamina C, Li S, Moffatt MF, Myers RH, Narisu N, Perry JRB, Peters MJ, Preuss M, Ripatti S, Rivadeneira F, Sandholt C, Scott LJ, Timpson NJ, Tyrer JP, van Wingerden S, Watanabe RM, White CC, Wiklund F, Barlassina C, Chasman DI, Cooper MN, Jansson J-O, Lawrence RW, Pellikka N, Prokopenko I, Shi J, Thiering E, Alavere H, Alibrandi MTS, Almgren P, Arnold AM, Aspelund T, Atwood LD, Balkau B, Balmforth AJ, Bennett AJ, Ben-Shlomo Y, Bergman RN, Bergmann S, Biebermann H, Blakemore AIF, Boes T, Bonnycastle LL, Bornstein SR, Brown MJ, Buchanan TA, Busonero F, Campbell H, Cappuccio FP, Cavalcanti-Proenca C, Chen Y-DI, Chen C-M, Chines PS, Clarke R, Coin L, Connell J, Day INM, Heijer Md, Duan J, Ebrahim S, Elliott P, Elosua R, Eiriksdottir G, Erdos MR, Eriksson JG, Facheris MF, Felix SB, Fischer-Posovszky P, Folsom AR, Friedrich N, Freimer NB, Fu M, Gaget S, Gejman PV, Geus EJC, Gieger C, Gjesing AP, Goel A, Goyette P, Grallert H, Graszler J, Greenawalt DM, Groves CJ, Gudnason V, Guiducci C, Hartikainen A-L, Hassanali N, Hall AS, Havulinna AS, Hayward C, Heath AC, Hengstenberg C, Hicks AA, Hinney A, Hofman A, Homuth G, Hui J, Igl W, Iribarren C, Isomaa B, Jacobs KB, Jarick I, Jewell E, John U, Jorgensen T, Jousilahti P, Jula A, Kaakinen M, Kajantie E, Kaplan LM, Kathiresan S, Kettunen J, Kinnunen L, Knowles JW, Kolcic I, Konig IR, Koskinen S, Kovacs P, Kuusisto J, Kraft P, Kvaloy K, Laitinen J, Lantieri O, Lanzani C, Launer LJ, Lecoeur C, Lehtimaki T, Lettre G, Liu J, Lokki M-L, Lorentzon M, Luben RN, Ludwig B, Manunta P, Marek D, Marre M, Martin NG, McArdle WL, McCarthy A, McKnight B, Meitinger T, Melander O, Meyre D, Midthjell K, Montgomery GW, Morken MA, Morris AP, Mulic R, Ngwa JS, Nelis M, Neville MJ, Nyholt DR, O’Donnell CJ, O’Rahilly S, Ong KK, Oostra B, Pare G, Parker AN, Perola M, Pichler I, Pietilainen KH, Platou CGP, Polasek O, Pouta A, Rafelt S, Raitakari O, Rayner NW, Ridderstrale M, Rief W, Ruokonen A, Robertson NR, Rzehak P, Salomaa V, Sanders AR, Sandhu MS, Sanna S, Saramies J, Savolainen MJ, Scherag S, Schipf S, Schreiber S, Schunkert H, Silander K, Sinisalo J, Siscovick DS, Smit JH, Soranzo N, Sovio U, Stephens J, Surakka I, Swift AJ, Tammesoo M-L, Tardif J-C, Teder-Laving M, Teslovich TM, Thompson JR, Thomson B, Tonjes A, Tuomi T, van Meurs JBJ, van Ommen G-J, Vatin V, Viikari J, Visvikis-Siest S, Vitart V, Vogel CIG, Voight BF, Waite LL, Wallaschofski H, Walters GB, Widen E, Wiegand S, Wild SH, Willemsen G, Witte DR, Witteman JC, Xu J, Zhang Q, Zgaga L, Ziegler A, Zitting P, Beilby JP, Farooqi IS, Hebebrand J, Huikuri HV, James AL, Kahonen M, Levinson DF, Macciardi F, Nieminen MS, Ohlsson C, Palmer LJ, Ridker PM, Stumvoll M, Beckmann JS, Boeing H, Boerwinkle E, Boomsma DI, Caulfield MJ, Chanock SJ, Collins FS, Cupples LA, Smith GD, Erdmann J, Froguel P, Gronberg H, Gyllensten U, Hall P, Hansen T, Harris TB, Hattersley AT, Hayes RB, Heinrich J, Hu FB, Hveem K, Illig T, Jarvelin M-R, Kaprio J, Karpe F, Khaw K-T, Kiemeney LA, Krude H, Laakso M, Lawlor DA, Metspalu A, Munroe PB, Ouwehand WH, Pedersen O, Penninx BW, Peters A, Pramstaller PP, Quertermous T, Reinehr T, Rissanen A, Rudan I, Samani NJ, Schwarz PEH, Shuldiner AR, Spector TD, Tuomilehto J, Uda M, Uitterlinden A, Valle TT, Wabitsch M, Waeber G, Wareham NJ, Watkins H, Wilson JF, Wright AF, Zillikens MC, Chatterjee N, McCarroll SA, Purcell S, Schadt EE, Visscher PM, Assimes TL, Borecki IB, Deloukas P, Fox CS, Groop LC, Haritunians T, Hunter DJ, Kaplan RC, Mohlke KL, O’Connell JR, Peltonen L, Schlessinger D, Strachan DP, van Duijn CM, Wichmann HE, Frayling TM, Thorsteinsdottir U, Abecasis GR, Barroso I, Boehnke M, Stefansson K, North KE, I McCarthy M, Hirschhorn JN, Ingelsson E, Loos RJF. Association analyses of 249,796 individuals reveal 18 new loci associated with body mass index. Nat Genet. 2010;42:937–948. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andreasen CH, Stender-Petersen KL, Mogensen MS, Torekov SS, Wegner L, Andersen G, Nielsen AL, Albrechtsen A, Borch-Johnsen K, Rasmussen SS, Clausen JO, Sandbaek A, Lauritzen T, Hansen L, Jørgensen T, Pedersen O, Hansen T. Low physical activity accentuates the effect of the FTO rs9939609 polymorphism on body fat accumulation. Diabetes. 2008;57:95–101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 5P30DK46200/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA087969/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- EY015473/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA055075/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK070756/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK046200/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA155626/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY015473/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL088521/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK080140/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK46200/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54CA155626/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL073168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL34594/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK058845/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004728/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- CA87969/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK58845/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL088521/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK091718/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA49449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HG004399/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- DK091718/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK080140/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL034594/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HG004728-02/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071981/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007703/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA049449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA055075/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL073168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA049449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL071981/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004399/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- DK70756/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

