Role of genes linked to sporadic Alzheimer's disease risk in the production of β-amyloid peptides
- PMID: 22949636
- PMCID: PMC3458335
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1201632109
Role of genes linked to sporadic Alzheimer's disease risk in the production of β-amyloid peptides
Abstract
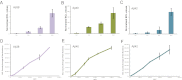
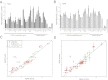
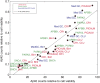
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is characterized by the presence of toxic protein aggregates or plaques composed of the amyloid β (Aβ) peptide. Various lengths of Aβ peptide are generated by proteolytic cleavages of the amyloid precursor protein (APP). Mutations in many familial AD-associated genes affect the production of the longer Aβ42 variant that preferentially accumulates in plaques. In the case of sporadic or late-onset AD, which accounts for greater than 95% of cases, several genes are implicated in increasing the risk, but whether they also cause the disease by altering amyloid levels is currently unknown. Through loss of function studies in a model cell line, here RNAi-mediated silencing of several late onset AD genes affected Aβ levels is shown. However, unlike the genes underlying familial AD, late onset AD-susceptibility genes do not specifically alter the Aβ42/40 ratios and suggest that these genes probably contribute to AD through distinct mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Brookmeyer R, Johnson E, Ziegler-Graham K, Arrighi HM. Forecasting the global burden of Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's Dementia. 2007;3:186–191. - PubMed
-
- Frisoni GB, Hampel H, O’Brien JT, Ritchie K, Winblad B. Revised criteria for Alzheimer’s disease: What are the lessons for clinicians? Lancet Neurol. 2011;10:598–601. - PubMed
-
- Ankarcrona M, Mangialasche F, Winblad B. Rethinking Alzheimer’s disease therapy: Are mitochondria the key? J Alzheimers Dis. 2010;20(Suppl 2):S579–S590. - PubMed
-
- Mangialasche F, Solomon A, Winblad B, Mecocci P, Kivipelto M. Alzheimer’s disease: Clinical trials and drug development. Lancet Neurol. 2010;9:702–716. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

