Evidence for additive and interaction effects of host genotype and infection in malaria
- PMID: 22949651
- PMCID: PMC3479498
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1204945109
Evidence for additive and interaction effects of host genotype and infection in malaria
Abstract
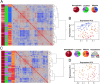
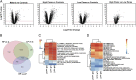
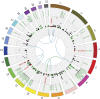
The host mechanisms responsible for protection against malaria remain poorly understood, with only a few protective genetic effects mapped in humans. Here, we characterize a host-specific genome-wide signature in whole-blood transcriptomes of Plasmodium falciparum-infected West African children and report a demonstration of genotype-by-infection interactions in vivo. Several associations involve transcripts sensitive to infection and implicate complement system, antigen processing and presentation, and T-cell activation (i.e., SLC39A8, C3AR1, FCGR3B, RAD21, RETN, LRRC25, SLC3A2, and TAPBP), including one association that validated a genome-wide association candidate gene (SCO1), implicating binding variation within a noncoding regulatory element. Gene expression profiles in mice infected with Plasmodium chabaudi revealed and validated similar responses and highlighted specific pathways and genes that are likely important responders in both hosts. These results suggest that host variation and its interplay with infection affect children's ability to cope with infection and suggest a polygenic model mounted at the transcriptional level for susceptibility.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
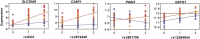
References
-
- Davila S, et al. International Meningococcal Genetics Consortium Genome-wide association study identifies variants in the CFH region associated with host susceptibility to meningococcal disease. Nat Genet. 2010;42:772–776. - PubMed
-
- Zhang FR, et al. Genomewide association study of leprosy. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:2609–2618. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

