Rescue of Notch signaling in cells incapable of GDP-L-fucose synthesis by gap junction transfer of GDP-L-fucose in Drosophila
- PMID: 22949680
- PMCID: PMC3458340
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1202369109
Rescue of Notch signaling in cells incapable of GDP-L-fucose synthesis by gap junction transfer of GDP-L-fucose in Drosophila
Abstract
Notch (N) is a transmembrane receptor that mediates cell-cell interactions to determine many cell-fate decisions. N contains EGF-like repeats, many of which have an O-fucose glycan modification that regulates N-ligand binding. This modification requires GDP-L-fucose as a donor of fucose. The GDP-L-fucose biosynthetic pathways are well understood, including the de novo pathway, which depends on GDP-mannose 4,6 dehydratase (Gmd) and GDP-4-keto-6-deoxy-D-mannose 3,5-epimerase/4-reductase (Gmer). However, the potential for intercellularly supplied GDP-L-fucose and the molecular basis of such transportation have not been explored in depth. To address these points, we studied the genetic effects of mutating Gmd and Gmer on fucose modifications in Drosophila. We found that these mutants functioned cell-nonautonomously, and that GDP-L-fucose was supplied intercellularly through gap junctions composed of Innexin-2. GDP-L-fucose was not supplied through body fluids from different isolated organs, indicating that the intercellular distribution of GDP-L-fucose is restricted within a given organ. Moreover, the gap junction-mediated supply of GDP-L-fucose was sufficient to support the fucosylation of N-glycans and the O-fucosylation of the N EGF-like repeats. Our results indicate that intercellular delivery is a metabolic pathway for nucleotide sugars in live animals under certain circumstances.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
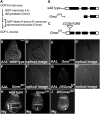
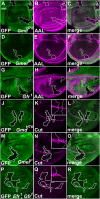
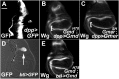
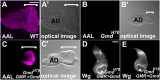

References
-
- Bishop JR, Schuksz M, Esko JD. Heparan sulphate proteoglycans fine-tune mammalian physiology. Nature. 2007;446:1030–1037. - PubMed
-
- Brückner K, Perez L, Clausen H, Cohen S. Glycosyltransferase activity of Fringe modulates Notch-Delta interactions. Nature. 2000;406:411–415. - PubMed
-
- Moloney DJ, et al. Fringe is a glycosyltransferase that modifies Notch. Nature. 2000;406:369–375. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

