Effects of high glucose on vascular endothelial growth factor synthesis and secretion in aortic vascular smooth muscle cells from obese and lean Zucker rats
- PMID: 22949809
- PMCID: PMC3431807
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms13089478
Effects of high glucose on vascular endothelial growth factor synthesis and secretion in aortic vascular smooth muscle cells from obese and lean Zucker rats
Abstract
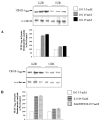
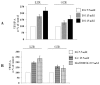
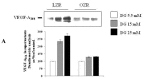
Type 1 diabetes is characterized by insulin deficiency, type 2 by both insulin deficiency and insulin resistance: in both conditions, hyperglycaemia is accompanied by an increased cardiovascular risk, due to increased atherosclerotic plaque formation/instabilization and impaired collateral vessel formation. An important factor in these phenomena is the Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF), a molecule produced also by Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells (VSMC). We aimed at evaluating the role of high glucose on VEGF-A(164) synthesis and secretion in VSMC from lean insulin-sensitive and obese insulin-resistant Zucker rats (LZR and OZR). In cultured aortic VSMC from LZR and OZR incubated for 24 h with d-glucose (5.5, 15 and 25 mM) or with the osmotic controls l-glucose and mannitol, we measured VEGF-A(164) synthesis (western, blotting) and secretion (western blotting and ELISA). We observed that: (i) d-glucose dose-dependently increases VEGF-A(164) synthesis and secretion in VSMC from LZR and OZR (n = 6, ANOVA p = 0.002-0.0001); (ii) all the effects of 15 and 25 mM d-glucose are attenuated in VSMC from OZR vs. LZR (p = 0.0001); (iii) l-glucose and mannitol reproduce the VEGF-A(164) modulation induced by d-glucose in VSMC from both LZR and OZR. Thus, glucose increases via an osmotic mechanism VEGF synthesis and secretion in VSMC, an effect attenuated in the presence of insulin resistance.
Keywords: diabetes; glucose; insulin resistance; lean zucker rats; obese zucker rats; osmotic stress; vascular endothelial growth factor; vascular smooth muscle cells.
Figures

References
-
- Wirostko B., Wong T.Y., Simò R. Vascular endothelial growth factor and diabetic complications. Progr. Retin. Eye Res. 2008;27:608–621. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N., Davis-Smith T. The biology of vascular endothelial growth factor. Endocr. Rev. 1997;18:4–25. - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P. Mechanisms of angiogenesis and arteriogenesis. Nat. Med. 2000;6:389–395. - PubMed
-
- Risau W. Mechanisms of angiogenesis. Nature. 1997;386:671–674. - PubMed
-
- Heil M., Schaper W. Pathophysiology of collateral development. Coron. Artery. Dis. 2004;15:373–378. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

