Metal-sulfate induced generation of ROS in human brain cells: detection using an isomeric mixture of 5- and 6-carboxy-2',7'-dichlorofluorescein diacetate (carboxy-DCFDA) as a cell permeant tracer
- PMID: 22949820
- PMCID: PMC3431818
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms13089615
Metal-sulfate induced generation of ROS in human brain cells: detection using an isomeric mixture of 5- and 6-carboxy-2',7'-dichlorofluorescein diacetate (carboxy-DCFDA) as a cell permeant tracer
Abstract
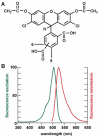
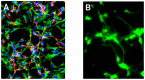
Evolution of reactive oxygen species (ROS), generated during the patho-physiological stress of nervous tissue, has been implicated in the etiology of several progressive human neurological disorders including Alzheimer's disease (AD) and amylotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). In this brief communication we used mixed isomers of 5-(and-6)-carboxy-2',7'-dichlorofluorescein diacetate (carboxy-DCFDA; C(25)H(14)C(l2)O(9); MW 529.3), a novel fluorescent indicator, to assess ROS generation within human neuronal-glial (HNG) cells in primary co-culture. We introduced pathological stress using the sulfates of 12 environmentally-, industrially- and agriculturally-relevant divalent and trivalent metals including Al, Cd, Cu, Fe, Hg, Ga, Mg, Mn, Ni, Pb, Sn and Zn. In this experimental test system, of all the metal sulfates analyzed, aluminum sulfate showed by far the greatest ability to induce intracellular ROS. These studies indicate the utility of using isomeric mixtures of carboxy-H(2)DCFDA diacetates as novel and highly sensitive, long-lasting, cell-permeant, fluorescein-based tracers for quantifying ROS generation in intact, metabolizing human brain cells, and in analyzing the potential epigenetic contribution of different metal sulfates to ROS-generation and ROS-mediated neurological dysfunction.
Keywords: 5-carboxy-2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein diacetate; 6-carboxy-2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein diacetate (5- and 6-carboxy-DCFDA; carboxy-DCFDA); Alzheimer’s disease; Parkinson’s disease; aluminum; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; carboxy-DCFDA; epigenetic human neural cells; inflammation; metal sulfates; prion disease; synergistic effects.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Induction of specific micro RNA (miRNA) species by ROS-generating metal sulfates in primary human brain cells.J Inorg Biochem. 2007 Sep;101(9):1265-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2007.06.004. Epub 2007 Jun 13. J Inorg Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17629564 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and Pro-Inflammatory Signaling in Human Brain Cells in Primary Culture.J Alzheimers Dis Parkinsonism. 2012 Jan 25;Suppl 2:001. doi: 10.4172/2161-0460.S2-0011. J Alzheimers Dis Parkinsonism. 2012. PMID: 24619568 Free PMC article.
-
Real time monitoring and quantification of reactive oxygen species in breast cancer cell line MCF-7 by 2',7'-dichlorofluorescin diacetate (DCFDA) assay.J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2018 Nov-Dec;94(Pt 1):26-33. doi: 10.1016/j.vascn.2018.03.007. Epub 2018 Apr 7. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2018. PMID: 29630935
-
Neurotoxicity of Metal Mixtures.Adv Neurobiol. 2017;18:227-265. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-60189-2_12. Adv Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 28889271 Review.
-
Heavy-metal-induced reactive oxygen species: phytotoxicity and physicochemical changes in plants.Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2014;232:1-44. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-06746-9_1. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 24984833 Review.
Cited by
-
Two-photon imaging of oxidative stress in living erythrocytes as a measure for human aging.Biomed Opt Express. 2020 Jun 2;11(7):3444-3454. doi: 10.1364/BOE.393898. eCollection 2020 Jul 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2020. PMID: 33014543 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of transcranial near-infrared photobiomodulation on cognitive outcomes in D-galactose/AlCl3 induced brain aging in BALB/c mice.Lasers Med Sci. 2022 Apr;37(3):1787-1798. doi: 10.1007/s10103-021-03433-8. Epub 2021 Oct 1. Lasers Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 34596786
-
Evaluation of oxidative stress biomarkers in Aiolopus thalassinus (Orthoptera: Acrididae) collected from areas polluted by the fertilizer industry.Ecotoxicology. 2017 Apr;26(3):340-350. doi: 10.1007/s10646-017-1767-6. Epub 2017 Jan 23. Ecotoxicology. 2017. PMID: 28116642
-
The oxidative stress response of the filamentous yeast Trichosporon cutaneum R57 to copper, cadmium and chromium exposure.Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip. 2014 Sep 3;28(5):855-862. doi: 10.1080/13102818.2014.965020. Epub 2014 Oct 21. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip. 2014. PMID: 26019570 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of In Vitro Cytotoxic, Genotoxic, Apoptotic, and Cell Cycle Arrest Potential of Iron-Nickel Alloy Nanoparticles.Toxics. 2022 Aug 24;10(9):492. doi: 10.3390/toxics10090492. Toxics. 2022. PMID: 36136457 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mariani E., Polidori M.C., Cherubini A., Mecocci P. Oxidative stress in brain aging, neurodegenerative and vascular diseases: An overview. J. Chromatogr. B. 2005;827:65–75. - PubMed
-
- Sasaki T. Analysis of aging-related oxidative stress status in normal aging animals and development of anti-aging interventions. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2010;130:29–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

