Protein interactions on telomeric retrotransposons in Drosophila
- PMID: 22949888
- PMCID: PMC3432853
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.4460
Protein interactions on telomeric retrotransposons in Drosophila
Abstract
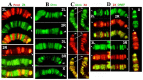
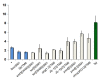
Telomere length in Drosophila is maintained by targeted transposition of three non-LTR retrotransposons: HeT-A, TART and TAHRE (HTT), but understanding the regulation of this process is hindered by our poor knowledge of HTT associated proteins. We have identified new protein components of the HTT array: Chromator (Chro), the TRF2/DREF complex and the sumoylation machinery. Chro was localized on telomeric HTT arrays by immunostaining, where it may interact with Prod directly, as indicated by yeast two-hybrid interaction, co-IP, and colocalization on polytene chromosomes. The TRF2/DREF complex may promote the open structure of HTT chromatin. The protein interactions controlling HTT chromatin structure and telomere length may be modulated by sumoylation.
Keywords: Chromator; Drosophila; Z4; chromatin; prod; putzig; retrotransposon; sumoylation; telomere.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Putzig partners DREF, TRF2 and KEN are involved in the regulation of the Drosophila telomere retrotransposons, HeT-A and TART.Mob DNA. 2013 Jul 3;4(1):18. doi: 10.1186/1759-8753-4-18. Mob DNA. 2013. PMID: 23822164 Free PMC article.
-
The chromosomal proteins JIL-1 and Z4/Putzig regulate the telomeric chromatin in Drosophila melanogaster.PLoS Genet. 2012;8(12):e1003153. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003153. Epub 2012 Dec 13. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 23271984 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila: Retrotransposons Making up Telomeres.Viruses. 2017 Jul 19;9(7):192. doi: 10.3390/v9070192. Viruses. 2017. PMID: 28753967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TAHRE, a novel telomeric retrotransposon from Drosophila melanogaster, reveals the origin of Drosophila telomeres.Mol Biol Evol. 2004 Sep;21(9):1620-4. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msh180. Epub 2004 Jun 2. Mol Biol Evol. 2004. PMID: 15175413
-
Silence at the End: How Drosophila Regulates Expression and Transposition of Telomeric Retroelements.J Mol Biol. 2020 Jul 10;432(15):4305-4321. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2020.06.004. Epub 2020 Jun 5. J Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32512004 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptional coupling of telomeric retrotransposons with the cell cycle.Sci Adv. 2025 Jan 3;11(1):eadr2299. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adr2299. Epub 2025 Jan 3. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 39752503 Free PMC article.
-
The hnRNP A1 homolog Hrb87F/Hrp36 is important for telomere maintenance in Drosophila melanogaster.Chromosoma. 2016 Jun;125(3):373-88. doi: 10.1007/s00412-015-0540-y. Epub 2015 Sep 16. Chromosoma. 2016. PMID: 26373285
-
The Hippo pathway as a target of the Drosophila DRE/DREF transcriptional regulatory pathway.Sci Rep. 2014 Nov 26;4:7196. doi: 10.1038/srep07196. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 25424907 Free PMC article.
-
The Putzig partners DREF, TRF2 and KEN are involved in the regulation of the Drosophila telomere retrotransposons, HeT-A and TART.Mob DNA. 2013 Jul 3;4(1):18. doi: 10.1186/1759-8753-4-18. Mob DNA. 2013. PMID: 23822164 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the Telomere elongation Mutation in Drosophila.Cells. 2022 Nov 3;11(21):3484. doi: 10.3390/cells11213484. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36359878 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andreyeva EN, Belyaeva ES, Semeshin VF, Pokholkova GV, Zhimulev IF. Three distinct chromatin domains in telomere ends of polytene chromosomes in Drosophila melanogaster Tel mutants. J Cell Sci. 2005;118(Pt 23):5465–77. - PubMed
-
- Török T, Benitez C, Takacs S, Biessmann H. The protein encoded by the gene proliferation disrupter (prod) is associated with the telomeric retrotransposon array in Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma. 2007;116(2):185–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

