Comparison of dexmedetomidine and remifentanil for attenuation of hemodynamic responses to laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation
- PMID: 22949979
- PMCID: PMC3427804
- DOI: 10.4097/kjae.2012.63.2.124
Comparison of dexmedetomidine and remifentanil for attenuation of hemodynamic responses to laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation
Abstract
Background: This study was designed to compare the effect of dexmedetomidine and remifentanil used in anesthetic induction on hemodynamic change after direct laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation.
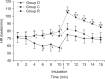
Methods: A total of 90 ASA class 1 or 2 patients were randomly assigned to one of 3 groups to receive one of the following treatments in a double-blind manner: normal saline (Group C, n = 30), dexmedetomidine 1 µg/kg (Group D, n = 30), remifentanil 1 µg/kg (Group R, n= 30). Anesthesia was induced with propofol 2 mg/kg and rocuronium 0.6 mg/kg and maintained with 2 vol% sevoflurane and 50% nitrous oxide in oxygen. In group D, dexmedetomidine 1 µg/kg was infused for 10 min before tracheal intubation. Patients in group R was received 1 µg/kg of remifentanil 1 minute before tracheal intubation. The systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure and heart rate were recorded from entrance to operation room to 5 min after tracheal intubation.
Results: The percent increase in systolic and diastolic blood pressure due to tracheal intubation in group D and R were significantly lower than that of group C (P < 0.05). The heart rate 1 min after tracheal intubation was lower in groups R and D than in the group C (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: In healthy normotensive patients, the use of dexmedetomidine during anesthetic induction suppressed a decrease in blood pressure due to anesthetic induction and blunted the hemodynamic responses to endotracheal intubation.
Keywords: Dexmedetomidine; Endotracheal intubation; Hemodynamics; Remifentanil.
Figures


References
-
- Shribman AJ, Smith G, Achola KJ. Cardiovascular and catecholamine responses to laryngoscopy with and without tracheal intubation. Br J Anaesth. 1987;59:295–299. - PubMed
-
- Edwards ND, Alford AM, Dobson PM, Peacock JE, Reilly CS. Myocardial ischaemia during tracheal intubation and extubation. Br J Anaesth. 1994;73:537–539. - PubMed
-
- Roy WL, Edelist G, Gilbert B. Myocardial ischemia during noncardiac surgical procedures in patients with coronary-artery disease. Anesthesiology. 1979;51:393–397. - PubMed
-
- Stoelting RK. Blood pressure and heart rate changes during short-duration laryngoscopy for tracheal intubation: influence of viscous or intravenous lidocaine. Anesth Analg. 1978;57:197–199. - PubMed
-
- Siedlecki J. Disturbances in the function of cardiovascular system in patients following endotracheal intubation and attempts of their prevention by pharmacological blockade of sympathetic system. Anaesth Resusc Intensive Ther. 1975;3:107–123. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

