Fine-mapping quantitative trait loci with a medium density marker panel: efficiency of population structures and comparison of linkage disequilibrium linkage analysis models
- PMID: 22950902
- PMCID: PMC3487687
- DOI: 10.1017/S0016672312000407
Fine-mapping quantitative trait loci with a medium density marker panel: efficiency of population structures and comparison of linkage disequilibrium linkage analysis models
Abstract
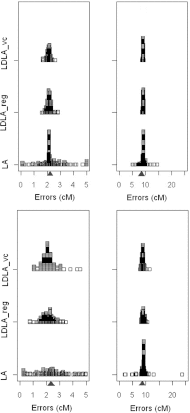
Recently, a Haley-Knott-type regression method using combined linkage disequilibrium and linkage analyses (LDLA) was proposed to map quantitative trait loci (QTLs). Chromosome of 5 and 25 cM with 0·25 and 0·05 cM, respectively, between markers were simulated. The differences between the LDLA approaches with regard to QTL position accuracy were very limited, with a significantly better mean square error (MSE) with the LDLA regression (LDLA_reg) in sparse map cases; the contrary was observed, but not significantly, in dense map situations. The computing time required for the LDLA variance components (LDLA_vc) model was much higher than the LDLA_reg model. The precision of QTL position estimation was compared for four numbers of half-sib families, four different family sizes and two experimental designs (half-sibs, and full- and half-sibs). Regarding the number of families, MSE values were lowest for 15 or 50 half-sib families, differences not being significant. We observed that the greater the number of progenies per sire, the more accurate the QTL position. However, for a fixed population size, reducing the number of families (e.g. using a small number of large full-sib families) could lead to less accuracy of estimated QTL position.
Figures
References
-
- Blott S., Kim J. J., Moisio S., Schmidt-Küntzel A., Cornet A., Berzi P., Cambisano N., Ford C., Grisart B., Johnson D., Karim L., Simon P., Snell R., Spelman R., Wong J., Georges M., Farnir F., Coppieters W.. Molecular dissection of a quantitative trait locus: a phenylanine-to-tyrosine substitution in the transmembrane domain of the bovine growth hormone receptor is associated with a major effect on milk yield and composition. Genetics. 2003;163:253–266. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Calus M., Meuwissen T. H. E., Winding J. J., Knol E. F., Schrooten C., Vereijken A., Veerkamp R. F.. Effects of the number of markers per haplotype and clustering of haplotypes on the accuracy of QTL mapping and prediction of genomic breeding values. Genetics Selection and Evolution. 2009;41:11–21. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cierco-Ayrolles C., Dejean S., Legarra A., Gilbert H., Druet T., Ytournel F., Estivals D., Oumouhou N., Mangin B.. Does probabilistic modelling of linkage disequilibrium evolution improve the accuracy of QTL location in animal pedigree? Genetics Selection and Evolution. 2010;42:38–48. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Druet T., Fritz S., Boussaha M., Ben-Jemaa S., Guillaume F., Derbala D., Zelenika D., Lechner D., Charon C., Boichard D., Gut I., Eggen A., Gautier M.. Fine mapping of quantitative trait loci affecting female fertility in dairy cattle on BTA03 using a dense single-nucleotide polymorphism map. Genetics. 2008;178:2227–2235. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Elsen J. M., Mangin B., Goffinet B., Boichard D., Le Roy P.. Alternative models for QTL detection in livestock. I. General introduction. Genetics Selection and Evolution. 1999;31:213–224.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

