VEGF-directed blood vessel patterning: from cells to organism
- PMID: 22951440
- PMCID: PMC3426816
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a006452
VEGF-directed blood vessel patterning: from cells to organism
Abstract
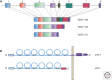
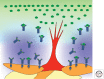
VEGF-A signaling is required for almost every aspect of vascular development, and it is a major regulator of vessel morphogenesis and patterning. VEGF-A perturbations are associated with severe vascular defects and lethality, and the pathway is coopted in pathological scenarios, including tumor angiogenesis. This review focuses on the roles of VEGF-A signaling during vessel development and patterning. I review the impact of VEGF-A signaling on endothelial cells in developing vessels, with emphasis on the importance of spatial regulation of several pathway components. I also discuss VEGF-A signaling patterns at the level of the vessel, with a focus on how polarity is set up and maintained in several vessel axes. The role of VEGF-A in patterning vessels relative to tissues and organs is also reviewed, with emphasis on neurovascular patterning and patterning at the embryonic midline.
Figures

References
-
- Ambler CA, Nowicki JL, Burke AC, Bautch VL 2001. Assembly of trunk and limb blood vessels involves extensive migration and vasculogenesis of somite-derived angioblasts. Dev Biol 234: 352–364 - PubMed
-
- Ambler CA, Schmunk GA, Bautch VL 2003. Stem cell-derived endothelial cells/progenitors migrate and pattern in the embryo using the VEGF signaling pathway. Dev Biol 257: 205–219 - PubMed
-
- Ashe H, Briscoe J 2006. The interpretation of morphogen gradients. Development 133: 385–394 - PubMed
-
- Bentley K, Gerhardt H, Bates P 2008. Agent-based simulation of Notch-mediated tip cell selection in angiogenic sprout initialisation. J Theor Biol 250: 25–36 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
