The IgA1 immune complex-mediated activation of the MAPK/ERK kinase pathway in mesangial cells is associated with glomerular damage in IgA nephropathy
- PMID: 22951891
- PMCID: PMC5177564
- DOI: 10.1038/ki.2012.192
The IgA1 immune complex-mediated activation of the MAPK/ERK kinase pathway in mesangial cells is associated with glomerular damage in IgA nephropathy
Abstract
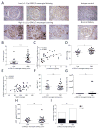
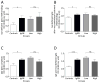
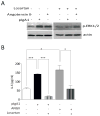
IgA nephropathy (IgAN), the most common primary glomerulonephritis worldwide, has significant morbidity and mortality as 20-40% of patients progress to end-stage renal disease within 20 years of onset. In order to gain insight into the molecular mechanisms involved in the progression of IgAN, we systematically evaluated renal biopsies from such patients. This showed that the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway was activated in the mesangium of patients presenting with over 1 g/day proteinuria and elevated blood pressure, but absent in biopsy specimens of patients with IgAN and modest proteinuria (<1 g/day). ERK activation was not associated with elevated galactose-deficient IgA1 or IgG specific for galactose-deficient IgA1 in the serum. In human mesangial cells in vitro, ERK activation through mesangial IgA1 receptor (CD71) controlled pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion and was induced by large-molecular-mass IgA1-containing circulating immune complexes purified from patient sera. Moreover, IgA1-dependent ERK activation required renin-angiotensin system as its blockade was efficient in reducing proteinuria in those patients exhibiting substantial mesangial activation of ERK. Thus, ERK activation alters mesangial cell-podocyte crosstalk, leading to renal dysfunction in IgAN. Assessment of MAPK/ERK activation in diagnostic renal biopsies may predict the therapeutic efficacy of renin-angiotensin system blockers in IgAN.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



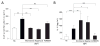


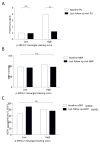
References
-
- Berger J, Hinglais N. Intercapillary deposits of IgA-IgG. J Urol Nephrol (Paris) 1968;74:694–695. - PubMed
-
- Monteiro RC, Moura IC, Launay P, et al. Pathogenic significance of IgA receptor interactions in IgA nephropathy. Trends Mol Med. 2002;8:464–468. - PubMed
-
- Coppo R, D’Amico G. Factors predicting progression of IgA nephropathies. J Nephrol. 2005;18:503–512. - PubMed
-
- Locatelli F, Marcelli D, Comelli M, et al. Proteinuria and blood pressure as causal components of progression to end-stage renal failure. Northern Italian Cooperative Study Group. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1996;11:461–467. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK082753/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM098539/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK075868/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- GM098539/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK078244/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK083663/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK083663/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK078244/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK075868/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK061525/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK082753/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK078244/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK061525/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

