Spontaneous formation of IpaB ion channels in host cell membranes reveals how Shigella induces pyroptosis in macrophages
- PMID: 22951981
- PMCID: PMC3461361
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2012.124
Spontaneous formation of IpaB ion channels in host cell membranes reveals how Shigella induces pyroptosis in macrophages
Abstract
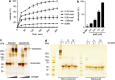
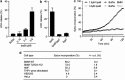
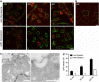
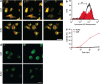
The Gram-negative bacterium Shigella flexneri invades the colonic epithelium and causes bacillary dysentery. S. flexneri requires the virulence factor invasion plasmid antigen B (IpaB) to invade host cells, escape from the phagosome and induce macrophage cell death. The mechanism by which IpaB functions remains unclear. Here, we show that purified IpaB spontaneously oligomerizes and inserts into the plasma membrane of target cells forming cation selective ion channels. After internalization, IpaB channels permit potassium influx within endolysosomal compartments inducing vacuolar destabilization. Endolysosomal leakage is followed by an ICE protease-activating factor-dependent activation of Caspase-1 in macrophages and cell death. Our results provide a mechanism for how the effector protein IpaB with its ion channel activity causes phagosomal destabilization and induces macrophage death. These data may explain how S. flexneri uses secreted IpaB to escape phagosome and kill the host cells during infection and, may be extended to homologs from other medically important enteropathogenic bacteria.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cholesterol is required to trigger caspase-1 activation and macrophage apoptosis after phagosomal escape of Shigella.Cell Microbiol. 2007 Jan;9(1):265-78. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2006.00787.x. Epub 2006 Aug 22. Cell Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 16925787
-
Structure-function analysis of the Shigella virulence factor IpaB.J Bacteriol. 2001 Feb;183(4):1269-76. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.4.1269-1276.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11157939 Free PMC article.
-
IpaB, a Shigella flexneri invasin, colocalizes with interleukin-1 beta-converting enzyme in the cytoplasm of macrophages.Infect Immun. 1997 Feb;65(2):787-93. doi: 10.1128/iai.65.2.787-793.1997. Infect Immun. 1997. PMID: 9009343 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of the virulence factor IpaB in Shigella spp. in the escape from immune cells and invasion of epithelial cells.Microbiol Res. 2015 Dec;181:43-51. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2015.08.006. Epub 2015 Sep 2. Microbiol Res. 2015. PMID: 26640051 Review.
-
The Many Faces of IpaB.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016 Feb 9;6:12. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2016.00012. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26904511 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Escherichia coli K88 activates NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis in vitro and in vivo.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2024 Feb 21;38:101665. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2024.101665. eCollection 2024 Jul. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2024. PMID: 38419757 Free PMC article.
-
Oligomeric states of the Shigella translocator protein IpaB provide structural insights into formation of the type III secretion translocon.Protein Sci. 2013 May;22(5):614-27. doi: 10.1002/pro.2245. Epub 2013 Mar 18. Protein Sci. 2013. PMID: 23456854 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular Shigella remodels its LPS to dampen the innate immune recognition and evade inflammasome activation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Nov 12;110(46):E4345-54. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1303641110. Epub 2013 Oct 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 24167293 Free PMC article.
-
T Cell Immunity to Bacterial Pathogens: Mechanisms of Immune Control and Bacterial Evasion.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 26;21(17):6144. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176144. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32858901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural Insights of Shigella Translocator IpaB and Its Chaperone IpgC in Solution.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Apr 29;11:673122. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.673122. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33996640 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maurelli AT, Sansonetti PJ. Genetic determinants of Shigella pathogenicity. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:127–150. - PubMed
-
- Zychlinsky A, Prevost MC, Sansonetti PJ. Shigella flexneri induces apoptosis in infected macrophages. Nature. 1992;358:167–169. - PubMed
-
- Sansonetti PJ, Phalipon A, Arondel J, Thirumalai K, Banerjee S, Akira S, et al. Caspase-1 activation of IL-1beta and IL-18 are essential for Shigella flexneri-induced inflammation. Immunity. 2000;12:581–590. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

