Minimally supervised multimodal exercise to reduce falls risk in economically and educationally disadvantaged older adults
- PMID: 22952201
- PMCID: PMC4127888
- DOI: 10.1123/japa.21.3.241
Minimally supervised multimodal exercise to reduce falls risk in economically and educationally disadvantaged older adults
Abstract
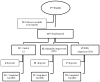
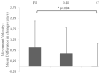
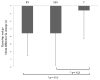
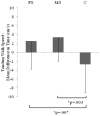
Few studies have evaluated the benefit of providing exercise to underprivileged older adults at risk for falls. Economically and educationally disadvantaged older adults with previous falls (mean age 79.06, SD = 4.55) were randomized to 4 mo of multimodal exercise provided as fully supervised center-based (FS, n = 45), minimally supervised home-based (MS, n = 42), or to nonexercise controls (C, n = 32). Comparing groups on the mean change in fall-relevant mobility task performance between baseline and 4 mo and compared with the change in C, both FS and MS had significantly greater reduction in timed up-and-go, F(2,73) = 5.82, p = .004, η2 p = .14, and increase in tandem-walk speed, F(2,73) = 7.71, p < .001 η2 p = .17. Change in performance did not statistically differ between FS and MS. In community-dwelling economically and educationally disadvantaged older adults with a history of falls, minimally supervised home-based and fully supervised center-based exercise programs may be equally effective in improving fall-relevant functional mobility.
Figures
References
-
- Ades PA. Medical progress: Cardiac rehabilitation and secondary prevention of coronary heart disease. New England Journal of Medicine. 2001;345(12):892–902. - PubMed
-
- American College of Sports and Medicine position Stand. Exercise and physical activity for older adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1998;39(8):1435–45. - PubMed
-
- Andresen EM, Wolinsky FD, Miller JP, Wilson MM, Malmstron TK, Miler DK. Cross-sectional and longitudinal risk-factors for falls, fear of falling and falls efficacy in a cohort of midle-aged African Americans. Gerontologist. 2006;46(2):249–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

