The sigma-1 receptor binds to the Nav1.5 voltage-gated Na+ channel with 4-fold symmetry
- PMID: 22952230
- PMCID: PMC3481303
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.382077
The sigma-1 receptor binds to the Nav1.5 voltage-gated Na+ channel with 4-fold symmetry
Abstract
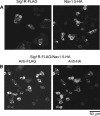
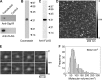
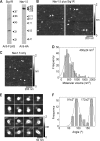
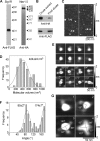
The sigma-1 receptor (Sig1R) is up-regulated in many human tumors and plays a role in the control of cancer cell proliferation and invasiveness. At the molecular level, the Sig1R modulates the activity of various ion channels, apparently through a direct interaction. We have previously shown using atomic force microscopy imaging that the Sig1R binds to the trimeric acid-sensing ion channel 1A with 3-fold symmetry. Here, we investigated the interaction between the Sig1R and the Nav1.5 voltage-gated Na(+) channel, which has also been implicated in promoting the invasiveness of cancer cells. We show that the Sig1R and Nav1.5 can be co-isolated from co-transfected cells, consistent with an intimate association between the two proteins. Atomic force microscopy imaging of the co-isolated proteins revealed complexes in which Nav1.5 was decorated by Sig1Rs. Frequency distributions of angles between pairs of bound Sig1Rs had two peaks, at ∼90° and ∼180°, and the 90° peak was about twice the size of the 180° peak. These results demonstrate that the Sig1R binds to Nav1.5 with 4-fold symmetry. Hence, each set of six transmembrane regions in Nav1.5 likely constitutes a Sig1R binding site, suggesting that the Sig1R interacts with the transmembrane regions of its partners. Interestingly, two known Sig1R ligands, haloperidol and (+)-pentazocine, disrupted the Nav1.5/Sig1R interaction both in vitro and in living cells. Finally, we show that endogenously expressed Sig1R and Nav1.5 also functionally interact.
Figures

References
-
- Monnet F. P. (2005) Sigma-1 receptor as regulator of neuronal intracellular Ca2+: clinical and therapeutic relevance. Biol. Cell 97, 873–883 - PubMed
-
- Aydar E., Palmer C. P., Klyachko V. A., Jackson M. B. (2002) The sigma receptor as a ligand-regulated auxiliary potassium channel subunit. Neuron 34, 399–410 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

