Rutin, a Flavonoid That Is a Main Component of Saussurea involucrata, Attenuates the Senescence Effect in D-Galactose Aging Mouse Model
- PMID: 22952557
- PMCID: PMC3431096
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/980276
Rutin, a Flavonoid That Is a Main Component of Saussurea involucrata, Attenuates the Senescence Effect in D-Galactose Aging Mouse Model
Abstract
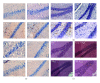
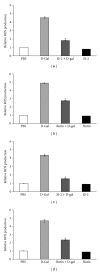
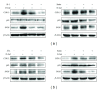
Saussurea involucrata (Kar. et Kir.), known as the snow lotus, grows in the Tian Shan and A'er Tai areas of China. It has recently been reported that the ethyl acetate extract of S. involucrata (SI-2) can inhibit proliferation and induce apoptosis in PC-3 human prostate cancer cells. This study investigated the protective effect of ethyl acetate extract of S. involucrata (SI-2) or rutin, a flavonoid extracted from ethyl acetate extract of S. involucrata (SI-2), on D-galactose- (D-gal-) induced brain injury in mice. Administering SI-2 or rutin (30 mg/kg/d and 30 mg/kg/d) for 6 weeks, concomitant with D-gal injection, significantly increased superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase activities and decreased the MDA level in plasma. Furthermore, the result showed that the percentages of cleaved caspase-3 and PARP in the D-gal-treated mice were much higher than those in the control. Pretreatment using SI-2 or rutin decreased the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 via downregulation of NF-kappaB, resulting in a decrease in lipid peroxidation. Furthermore, our results also showed that oral administration of rutin to these mice significantly improved behavioral performance in a step-through passive avoidance task and these results suggest that SI-2 or rutin exerts potent antiaging effects on D-gal in mice via antioxidative mechanisms.
Figures


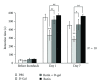
References
-
- Barnham KJ, Masters CL, Bush AI. Neurodegenerative diseases and oxidatives stress. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. 2004;3(3):205–214. - PubMed
-
- Finkel T, Holbrook NJ. Oxidants, oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature. 2000;408(6809):239–247. - PubMed
-
- Yin ST, Tang ML, Deng HM, et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate induced primary cultures of rat hippocampal neurons death linked to calcium overload and oxidative stress. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Archives of Pharmacology. 2009;379(6):551–564. - PubMed
-
- Valko M, Leibfritz D, Moncol J, Cronin MTD, Mazur M, Telser J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. International Journal of Biochemistry and Cell Biology. 2007;39(1):44–84. - PubMed
-
- Floyd RA, Soong LM, Stuart MA, Reight DL. Free radicals and carcinogenesis. Some properties of the nitroxyl free radicals produced by covalent binding of 2-nitrosofluorene to unsaturated lipids of membranes. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics. 1978;185(2):450–457. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

