Deep sequencing and microarray hybridization identify conserved and species-specific microRNAs during somatic embryogenesis in hybrid yellow poplar
- PMID: 22952685
- PMCID: PMC3430688
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043451
Deep sequencing and microarray hybridization identify conserved and species-specific microRNAs during somatic embryogenesis in hybrid yellow poplar
Abstract
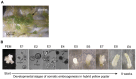
Background: To date, several studies have indicated a major role for microRNAs (miRNAs) in regulating plant development, but miRNA-mediated regulation of the developing somatic embryo is poorly understood, especially during early stages of somatic embryogenesis in hardwood plants. In this study, Solexa sequencing and miRNA microfluidic chips were used to discover conserved and species-specific miRNAs during somatic embryogenesis of hybrid yellow poplar (Liriodendron tulipifera×L. chinense).
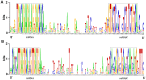
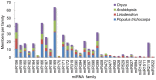
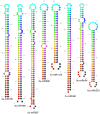
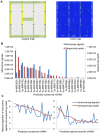
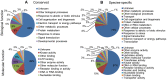
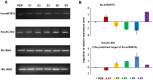
Methodology/principal findings: A total of 17,214,153 reads representing 7,421,623 distinct sequences were obtained from a short RNA library generated from small RNAs extracted from all stages of somatic embryos. Through a combination of deep sequencing and bioinformatic analyses, we discovered 83 sequences with perfect matches to known miRNAs from 33 conserved miRNA families and 273 species-specific candidate miRNAs. MicroRNA microarray results demonstrated that many conserved and species-specific miRNAs were expressed in hybrid yellow poplar embryos. In addition, the microarray also detected another 149 potential miRNAs, belonging to 29 conserved families, which were not discovered by deep sequencing analysis. The biological processes and molecular functions of the targets of these miRNAs were predicted by carrying out BLAST search against Arabidopsis thaliana GenBank sequences and then analyzing the results with Gene Ontology.
Conclusions: Solexa sequencing and microarray hybridization were used to discover 232 candidate conserved miRNAs from 61 miRNA families and 273 candidate species-specific miRNAs in hybrid yellow poplar. In these predicted miRNAs, 64 conserved miRNAs and 177 species-specific miRNAs were detected by both sequencing and microarray hybridization. Our results suggest that miRNAs have wide-ranging characteristics and important roles during all stages of somatic embryogenesis in this economically important species.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Voinnet O (2009) Origin, biogenesis, and activity of plant microRNAs. Cell 136: 669–687. - PubMed
-
- Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP, Bartel B (2006) MicroRNAs and their regulatory roles in plants. Annual Review of Plant Biology. Palo Alto: Annual Reviews. pp. 19–53. - PubMed
-
- Chuck G, Candela H, Hake S (2009) Big impacts by small RNAs in plant development. Current Opinion in Plant Biology 12: 81–86. - PubMed
-
- Oh TJ, Wartell RM, Cairney J, Pullman GS (2008) Evidence for stage-specific modulation of specific microRNAs (miRNAs) and miRNA processing components in zygotic embryo and female gametophyte of loblolly pine (Pinus taeda). New Phytologist 179: 67–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

