Decline in HIV prevalence among young men in the general population of Cotonou, Benin, 1998-2008
- PMID: 22952773
- PMCID: PMC3429516
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043818
Decline in HIV prevalence among young men in the general population of Cotonou, Benin, 1998-2008
Abstract
Objective: To assess changes in the prevalence of HIV and other sexually transmitted infections, as well as in different proximal and distal factors related to HIV infection, in the general population of Cotonou between 1998 and 2008, while an intensive preventive intervention targeting the sex work milieu was ongoing.
Methods: A two-stage cluster sampling procedure was used to select the participants in each study. Subjects aged 15-49 who agreed to participate were interviewed and tested for HIV, syphilis, HSV-2, gonorrhoea and chlamydia. We used the Roa-Scott Chi-square test (proportions) and the Student's t test (means) for bivariate comparisons, and adjusted logistic regression models taking into account the cluster effect for multivariate analyses.
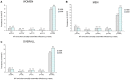
Results: HIV prevalence decreased significantly in men (3.4% in 1998 versus 2.0% in 2008, p = 0.048), especially in those aged 15-29 (3.0% to 0.5%, p = 0.002). Among men, the prevalence of gonorrhoea decreased significantly (1.1% to 0.3%, p = 0.046) while HSV-2 prevalence increased from 12.0% to 18.1% (p = 0.0003). The proportion of men who reported condom use at least once (29.3% to 61.0%, p<0.0001) and of those having attained a secondary educational level or more (17.1% to 61.3%, p<0.0001) also increased significantly. There was an overall decrease in the prevalence of syphilis (1.5% to 0.6%, p = 0.0003).
Conclusion: This is the first population-based study reporting a significant decline in HIV prevalence among young men in an African setting where overall prevalence has never reached 5%. The decline occurred while preventive interventions targeting the sex work milieu were ongoing and the educational level was increasing.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO), Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) (2011) Progress report 2011: Global HIV/AIDS response – Epidemic update and health sector progress towards universal access Geneva Available: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2011/9789241502986_eng.pdf Accessed 2012 April 20.
-
- Gregson S, Garnett GP, Nyamukapa CA, Hallett TB, Lewis JJ, et al. (2006) HIV decline associated with behavior change in eastern Zimbabwe. Science 311: 664–666. - PubMed
-
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (2010) UNAIDS Report on the Global AIDS Epidemic 2010. Geneva. Available: http://www.unaids.org/globalreport/Global_report.htm. Accessed 2011 December 30.
-
- Benoit SN, Gershy-Damet GM, Coulibaly A, Koffi K, Sangare VS, et al. (1990) Seroprevalence of HIV infection in the general population of the Cote d’Ivoire, West Africa. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 3: 1193–1196. - PubMed
-
- Institut national de la statistique (INS), Ministère de la lutte contre le SIDA (MLS), et ORC Macro (2005) Enquête sur les indicateurs du SIDA, Côte d’Ivoire. Claverton, Maryland, USA: INS et ORC Macro. Available: http://pdf.usaid.gov/pdf_docs/PNADG727.pdf. Assessed 2012 June 10.

